G4280
Anti-Guanylyl Cyclase α1 antibody produced in rabbit

IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Synonyme(s) :
Anti-GC-S-alpha-1, Anti-GC-SA3, Anti-GCS-alpha-3, Anti-GUC1A3, Anti-GUCA3, Anti-GUCSA3, Anti-GUCY1A3, Anti-MYMY6
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
rabbit
Conjugué
unconjugated
Forme d'anticorps
IgG fraction of antiserum
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
polyclonal
Forme
buffered aqueous solution
Poids mol.
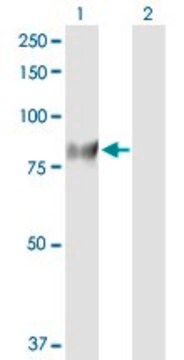
~80 kDa
Espèces réactives
mouse, rat, human, bovine
Conditionnement
antibody small pack of 25 μL
Validation améliorée
independent
Learn more about Antibody Enhanced Validation
Technique(s)
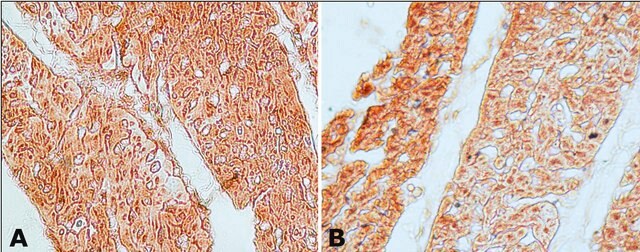
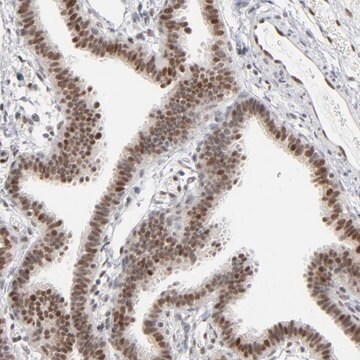
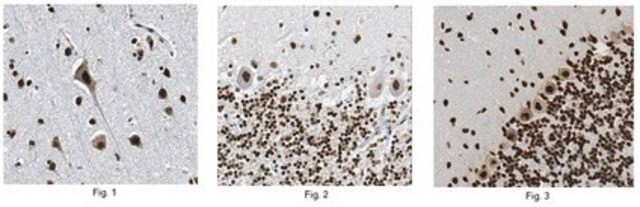
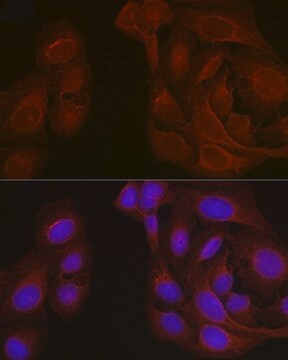
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:100 using trypsin-treated human, bovine and mouse heart tissue
immunoprecipitation (IP): 5-10 μg using 60-120 μg of a cytosolic fraction of rat brain
western blot: 1:10,000 using cytosolic fraction of rat brain
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Modification post-traductionnelle de la cible
unmodified
Informations sur le gène
human ... GUCY1A3(2982)
mouse ... Gucy1a3(60596)
rat ... Gucy1a3(497757)
Description générale
Immunogène
Application
It was used as a primary antibody for immunohistochemical:
- localization of α1 subunits of sGC (soluble guanylate cyclase) in the guinea pig gastrointestinal tract
- detection of expression of sGC in the vasculature of rat skeletal muscle
- localization of the functional subunit of NO receptors, sGCα1 in guinea pig caecum
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Forme physique
Clause de non-responsabilité
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique