270555
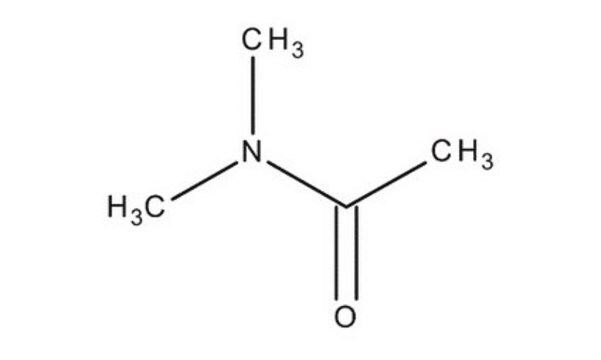
N,N-diméthylacétamide
suitable for HPLC, ≥99.9%
About This Item
4 mmHg ( 38 °C)
Produits recommandés
Densité de vapeur
3 (vs air)
Niveau de qualité
Pression de vapeur
2 mmHg ( 25 °C)
4 mmHg ( 38 °C)
Essai
≥99.9%
Forme
liquid
Température d'inflammation spontanée
914 °F
Limite d'explosivité
1.8 %, 100 °F
11.5 %, 160 °F
Technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
Impuretés
<0.030% water
Résidus d'évap.
<0.001%
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.437 (lit.)
pH
4 (20 °C, 200 g/L)
pb
164.5-166 °C (lit.)
Pf
−20 °C (lit.)
Densité
0.937 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
λ
H2O reference
Absorption UV
λ: 270 nm Amax: 1.00
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.30
λ: 290 nm Amax: 0.15
λ: 310 nm Amax: 0.05
λ: 320 nm Amax: 0.03
λ: 360-400 nm Amax: 0.01
Application(s)
food and beverages
Chaîne SMILES
CN(C)C(C)=O
InChI
1S/C4H9NO/c1-4(6)5(2)3/h1-3H3
Clé InChI
FXHOOIRPVKKKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Application
- Ternary Phase-Field Simulation of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Microporous Membrane Structures Prepared by Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation with Different Additives and Solvent Treatments: This study highlights the use of N,N-Dimethylacetamide (DMAC) in the preparation of advanced poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes, showcasing its critical role in enhancing polymer processing and membrane structures in material science (Zhang et al., 2024).
- Improved Protein Removal Performance of PES Hollow-Fiber Ultrafiltration Membrane with Sponge-like Structure: Research demonstrates DMAC′s effectiveness in the production of high-performance ultrafiltration membranes, emphasizing its importance in biomedical applications and wastewater treatment (Zhao et al., 2024).
- Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Aerogels with alpha, beta, and gamma; Crystalline Forms: Correlating Physicochemical Properties with Polymorphic Structures: This article showcases the versatility of DMAC as a solvent in the synthesis of poly(vinylidene fluoride) aerogels, linking its use to significant advancements in the understanding of polymer crystallinity and properties (Suresh et al., 2024).
- Cellulose Esters: Synthesis for Further Formation of Films with Magnetite Nanoparticles Incorporated: The study leverages DMAC for the synthesis of advanced cellulose ester films integrated with magnetite nanoparticles, illustrating its potential in developing multifunctional materials for diverse industrial applications (Furlan Sandrini et al., 2024).
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Eye Irrit. 2 - Repr. 1B
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
147.2 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
64 °C - closed cup
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique