SCC469
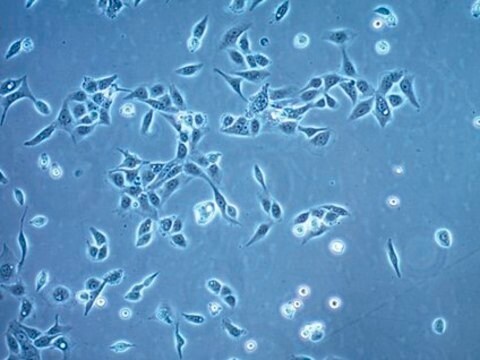
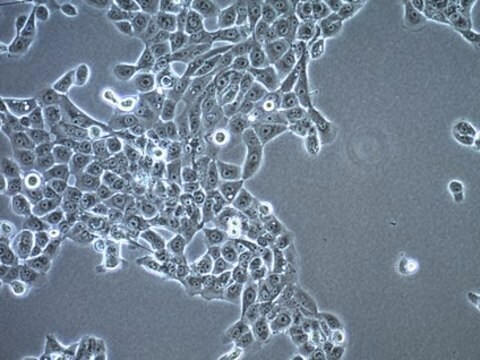
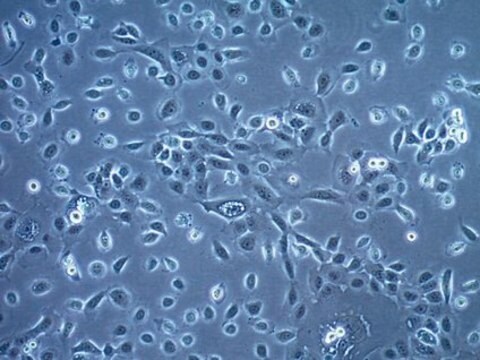
MOC1 Mouse Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) Cell Line
Mouse
Synonyme(s) :
MOC2 cell line, mouse oral carcinoma 2 cell line, oral carcinoma cell line
About This Item
Produits recommandés
product name
MOC1 Mouse Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) Cell Line,
Source biologique
mouse
Niveau de qualité
Conditionnement
vial of ≥1X10⁶ cells/vial vials
Fabricant/nom de marque
Millipore
Technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
Conditions d'expédition
liquid nitrogen
Température de stockage
−196°C
Application
- Each vial contains >1X106 viable cells.
- MOC1 cells are verified to be of mouse origin and negative for human, rat, Chinese hamster, Golden Syrian hamster, and non-human primate interspecies contamination, as assessed by a Contamination Clear panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services
- Cells tested negative for infectious diseases against a Mouse Essential CLEAR panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.
- Cells tested negative for mycoplasma.
Caractéristiques et avantages
Description de la cible
Stockage et stabilité
Clause de non-responsabilité
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique