ABS1646
Anti-VPS4A (UT289)
serum, from rabbit
Synonyme(s) :
Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4A, Protein SKD2, SKD1-homolog, Vacuolar protein sorting factor 4A, Vacuolar sorting protein 4, VPS4A
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
rabbit
Niveau de qualité
Forme d'anticorps
serum
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
polyclonal
Espèces réactives
human, mouse
Technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
Numéro d'accès NCBI
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Conditions d'expédition
ambient
Modification post-traductionnelle de la cible
unmodified
Informations sur le gène
human ... VPS4A(27183)
mouse ... Vps4A(116733)
Description générale
Spécificité
Immunogène
Application
Immunoprecipitation Analysis: A representative lot immunoprecipited EGFP-VPS4A fusion together with CHMP5-Myc and Myc-LIP5 exogenously expressed in HEK293T cells. CHMP5-Myc with L4D mutation and Myc-LIP5 with M64A, W147D, or Y278A mutation failed to co-immunoprecipitate with VPS4A (Skalicky, J.J., et al. (2012). J. Biol. Chem. 287(52):43910-43926).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected both endogenous VPS4A and exogenously expressed EGFP-VPS4A fusion in HEK293T cell lysates as well as in Anti-Myc immunoprecipites from CHMP5-Myc or Myc-LIP5 expressing cells (Skalicky, J.J., et al. (2012). J. Biol. Chem. 287(52):43910-43926).
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected the VPS4A target band in lysate from untransfected, but not VPS4A shRNA-transfected, HeLa cells (Morita, E., et al. (2010). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107(29):12889-12894).
Signaling
Qualité
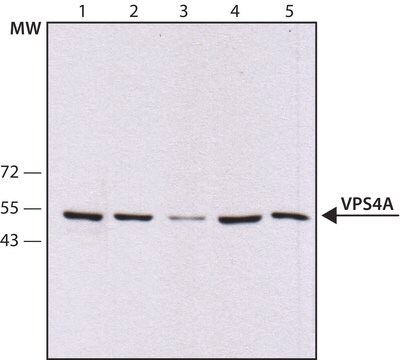
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:1,000 dilution of this antiserum detected VPS4A in 10 µg of MCF-7 cell lysate.
Description de la cible
Forme physique
Stockage et stabilité
Handling Recommendations: Upon receipt and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Autres remarques
Clause de non-responsabilité
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique