Description générale
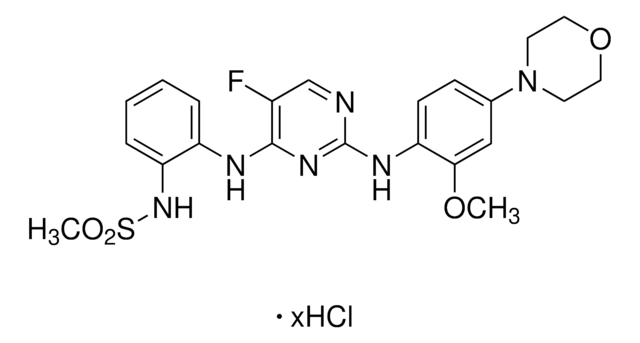
A cell-permeable, ATP competitive, potent, and selective LRRK2 inhibitor (IC50 of 13 nM, 6 nM, and 2.45 µM for wild type, G2019S mutant, and drug resistant A2016T mutant LRRK2, respectively, in an in vitro ATP-site competititon binding assay). While it is shown to inhibit DCLK2 (IC50 = 45 nM) and suppress MAPK7 autophosphorylation (EC50 = 160 nM), this compound (<10 µM) demonstrates very good overall selectivity, targeting 12 out of 442 other kinases in a kinase-binding and biochemical assay. At 0.05–3 µM, it induces dose-dependent inhibition of Ser910 and Ser935 phosphorylation accompanied by loss of 14-3-3 binding to both wild-type LRRK2 and LRRK2[G2019S] in stably transfected HEK293 cells, but not in the drug-resistant LRRK2[A2016T] and LRRK2[A2016T + G2019S] mutants. Similar effects on endogenous LRRK2 phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding can be observed in human lympho¬blastoid cells and for the LRRK2 G2019S mutant derived from a Parkinson′s disease patient, and in human-derived neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cells, as well as in mouse Swiss 3T3 cells. 100 mg/kg of compound injected into mice elicits complete Ser910 and Ser935 dephosphorylation of LRRK2 in the kidney, but not in the brain which may result from an inability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. In addition, it promotes relocalization of LRRK2 to more aggregate and fibrillar-like structures.
A cell-permeable, ATP competitive, potent, and selective LRRK2 inhibitor (IC50 of 13 nM, 6 nM, and 2.45 µM for wild type, G2019S mutant, and drug resistant A2016T mutant LRRK2, respectively, in an in vitro ATP-site competititon binding assay). While it is shown to inhibit DCLK2 (IC50 = 45 nM) and suppress MAPK7 autophosphorylation (EC50 = 160 nM), this compound (<10 µM) demonstrates very good overall selectivity, targeting 12 out of 442 other kinases in a kinase-binding and biochemical assay. At 0.05-3 µM, it induces dose-dependent inhibition of Ser910 and Ser935 phosphorylation accompanied by loss of 14-3-3 binding to both wild-type LRRK2 and LRRK2[G2019S] in stably transfected HEK293 cells, but not in the drug-resistant LRRK2[A2016T] and LRRK2[A2016T + G2019S] mutants. Similar effects on endogenous LRRK2 phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding can be observed in human lympho-blastoid cells and for the LRRK2 G2019S mutant derived from a Parkinson′s disease patient, and in human-derived neuroblastoma SHSY5Y cells, as well as in mouse Swiss 3T3 cells. 100 mg/kg of compound injected into mice elicits complete Ser910 and Ser935 dephosphorylation of LRRK2 in the kidney, but not in the brain which may result from an inability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. In addition, it promotes relocalization of LRRK2 to more aggregate and fibrillar-like structures.
Autres remarques
Deng, X., et al. 2011. Nat. Chem. Biol.7, 203.