767344
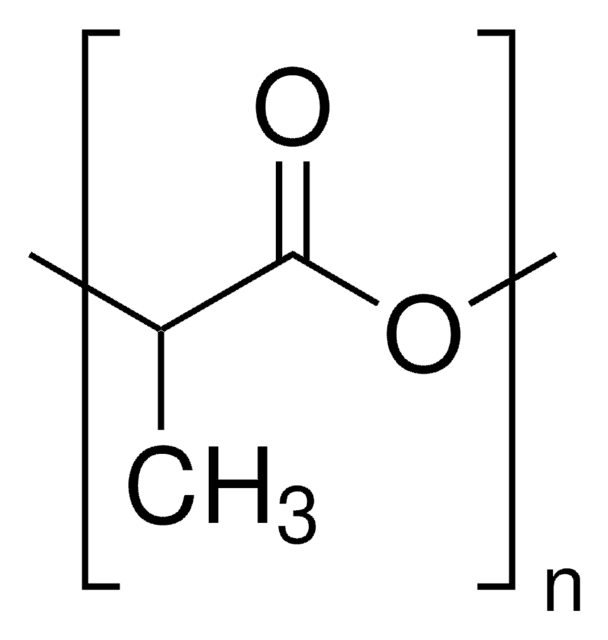
Poly(D,L-lactide)
average Mn 20,000 (NMR), PDI ≤1.3
Synonyme(s) :
PDLA, PLA, polyDL-lactide
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
crystals
Niveau de qualité
Poids mol.
average Mn 20,000 (NMR)
Intervalle de dégradation
<6 months
Pf
320-350 °C
PDI
≤1.3
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Application
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
Microparticle drug delivery systems have been extensively researched and applied to a wide variety of pharmaceutical and medical applications due to a number of advantages including injectability, local applicability to target tissues and sites, and controlled drug delivery over a given time period.
The world of commercial biomaterials has stagnated over the past 30 years as few materials have successfully transitioned from the bench to clinical use. Synthetic aliphatic polyesters have continued to dominate the field of resorbable biomaterials due to their long history and track record of approval with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique