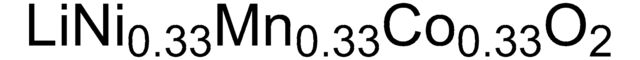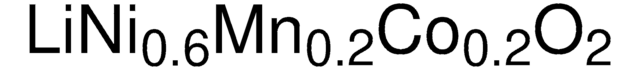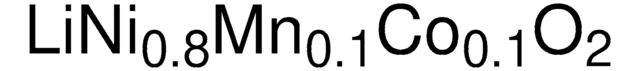765171
Lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxide
electrode sheet, aluminum substrate, size 5 in. × 10 in.
Synonyme(s) :
NCA
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
battery grade
Description
Nominal Voltage: 3.7 V, Li/Li+
Essai
≥98%
Composition
loading, ≥80%
Caractéristiques du produit alternatif plus écologique
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Ampleur du marquage
≥80% loading
Taille
5 in. × 10 in.
Épaisseur
12-25 μm
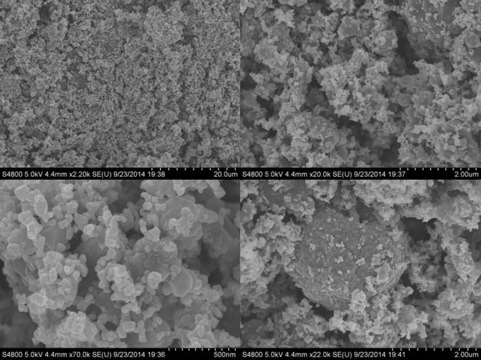
Taille des particules
10-13 μm (typical)
Capacité
150 mAh/g(minimum)
180 mAh/g(nominal at 0.1C)
Pf
>1000 °C
Application(s)
battery manufacturing
Autre catégorie plus écologique
, Enabling
Description générale
Application
The NCA casted electrode sheets can be cut into appropriate size and is ready to be used in lithium ion batteries.
Autres remarques
Operating Condiditons:
- Recommended maximum charge voltage: 4.3 V vs Li/Li+
- Recommended maximum charge current: 4C
- Recommended cut-off voltage for discharge: 3.0 V vs Li/Li+
- Recommended charge method: constant current - constant voltage
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Carc. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
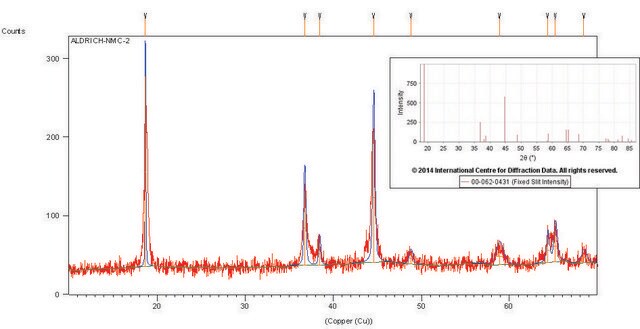
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Professor Qiao’s laboratory lays out recent advances in conversion type lithium metal fluoride batteries. This review explores key concepts in developing electrochemically stable microstructures for wide Li-ion insertion channels.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
The critical technical challenges associated with the commercialization of electric vehicle batteries include cost, performance, abuse tolerance, and lifespan.
Li-ion batteries are currently the focus of numerous research efforts with applications designed to reduce carbon-based emissions and improve energy storage capabilities.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique