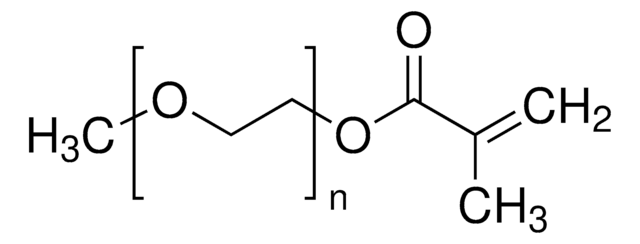
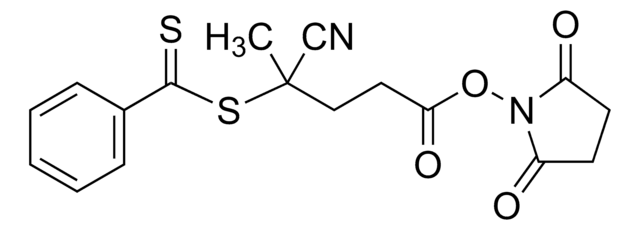
764930
Poly(ethylene glycol) 4-cyano-4-(phenylcarbonothioylthio)pentanoate
average Mn 10,000
Synonyme(s) :
PEG CTA, PEG RAFT
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Description
PEG average Mn 10,000 kDa; n~220
Niveau de qualité
Forme
solid
Poids mol.
average Mn 10,000
Pf
58-62 °C
PDI
≤1.1
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Skin Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization is rapidly moving to the forefront in construction of drug and gene delivery vehicles.
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
Humankind has utilized protein materials throughout its existence, starting with the use of materials such as wool and silk for warmth and protection from the elements and continuing with the use of recombinant DNA techniques to synthesize proteins with unique and useful properties.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique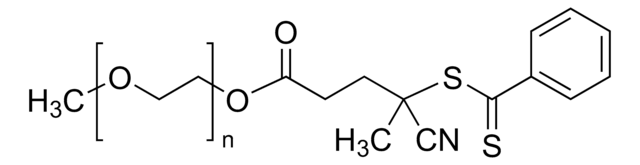
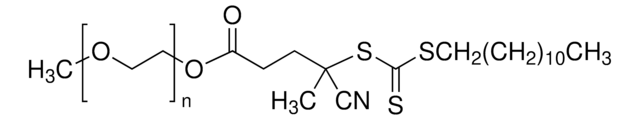
![Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether 4-cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoate average Mn 10,000](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/618/250/98532519-ae4b-4fc4-b6f0-fb15f144c8f1/640/98532519-ae4b-4fc4-b6f0-fb15f144c8f1.png)
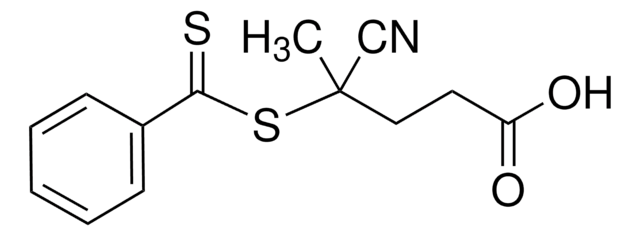
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)
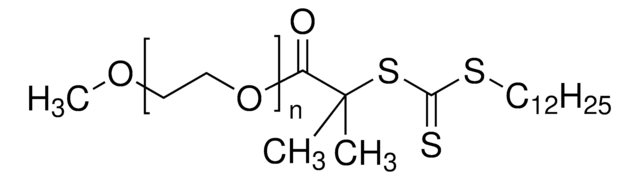
![Poly(ethylene glycol) bis[2-(dodecylthiocarbonothioylthio)-2-methylpropionate] average Mn 10,800](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/369/930/ba9a86e7-8635-4a23-aa7c-7db94c295272/640/ba9a86e7-8635-4a23-aa7c-7db94c295272.png)