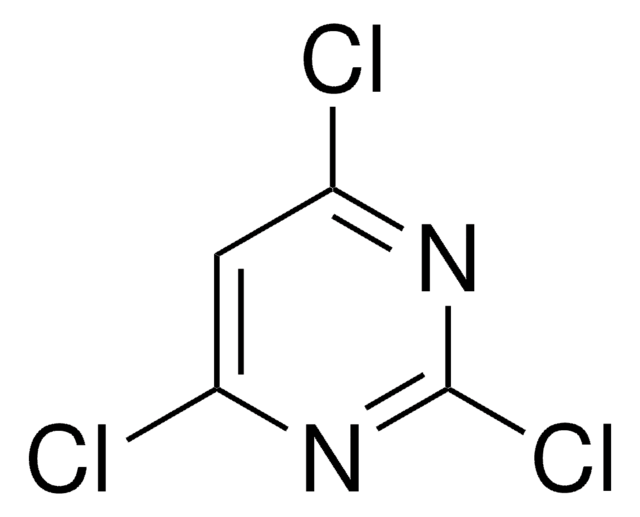
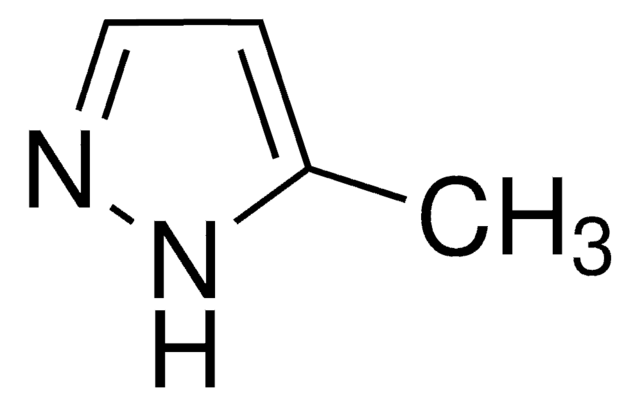
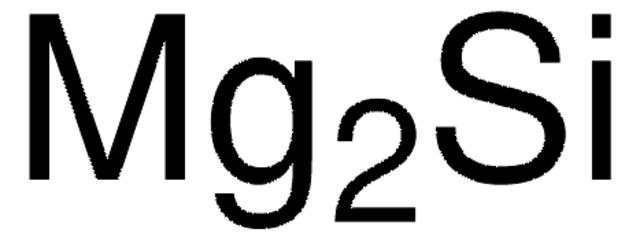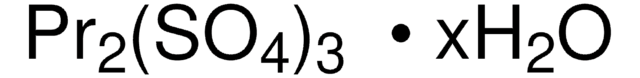752622
Iron disilicide
powder, -20 mesh, 99.9% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
Iron silicide
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
99.9% trace metals basis
Forme
powder
Caractéristiques du produit alternatif plus écologique
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Taille des particules
-20 mesh
Pf
1220 °C (lit.)
Autre catégorie plus écologique
, Enabling
InChI
1S/Fe.2H2Si/h;2*1H2
Clé InChI
UVUDQHYBXBVHAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
The price of tellurium, a key component in many thermoelectric materials, has risen in recent years, leading to the search for more cost-effective substitutes. This article presents silicide materials as a cheaper potential alternative.
In recent years, the price of tellurium, a key component in the bestperforming thermoelectric materials, has increased significantly, leading to the question, “Is it economically viable to produce thermoelectric generators on an industrial scale?
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique