729140
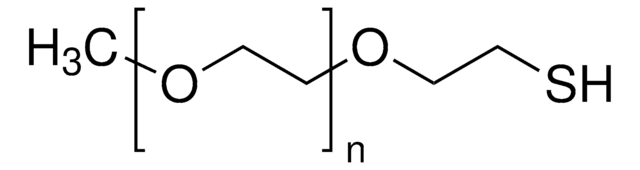
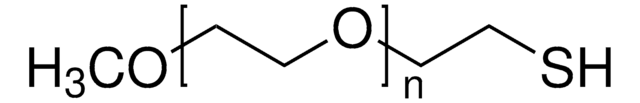
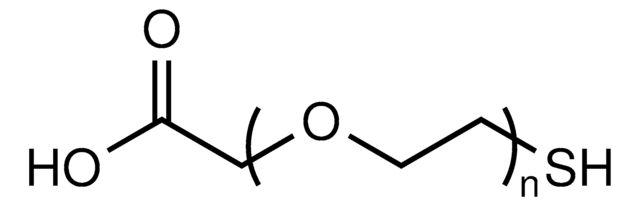
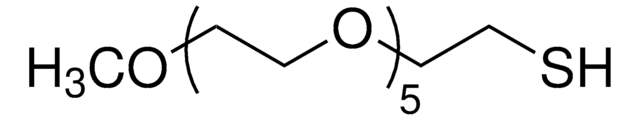
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether thiol
average Mn 2,000, chemical modification reagent thiol reactive, methoxy, thiol
Synonyme(s) :
Polyethylene glycol, Methoxy PEG thiol, Methoxypolyethylene glycol thiol, PEG thiol, mPEG thiol
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Nom du produit
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether thiol, average Mn 2,000
Forme
solid
Niveau de qualité
Poids mol.
average Mn 2,000
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: chemical modification reagent
reactivity: thiol reactive
Pf
50-55 °C
Extrémité Ω
thiol
Extrémité α
methoxy
Architecture des polymères
shape: linear
functionality: monofunctional
Température de stockage
−20°C
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Application
- Surface modification of polyaniline nanorods with thiol-terminated poly (ethylene oxide): This study explores the use of varying molecular weights of poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether thiol for modifying the surface of polyaniline nanorods, aiming to enhance their dispersibility and functionality (DiTullio et al., 2018).
- Colorimetric determination of p-phenylenediamine using silver nanoparticles modified with poly (ethylene glycol) methyl ether thiol: The research demonstrates the use of poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether thiol in modifying silver nanoparticles for the colorimetric determination of p-phenylenediamine, showcasing its application in analytical chemistry (Lee et al., 2017).
- Facile synthesis and self-assembly of amphiphilic polydimethylsiloxane with poly (ethylene glycol) moieties via thiol-ene click reaction: This article discusses the synthesis and self-assembly of amphiphilic copolymers using thiol-ene click chemistry, emphasizing the versatility of poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether thiol in creating functional materials (Xia et al., 2015).
- Determination of polyethylene glycol end group functionalities by combination of selective reactions and characterization by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS): This study highlights a method for characterizing end group functionalities of poly(ethylene glycol) derivatives using MALDI-TOF MS, where poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether thiol plays a critical role in the analysis process (Zhang et al., 2014).
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organes cibles
Respiratory system
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique