700428
N,N-Dimethylformamide-d7
≥99.5 atom % D, contains 0.03 % (v/v) TMS
Synonyme(s) :
DMF-d7, Heptadeutero-N,N-dimethylformamide
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Pureté isotopique
≥99.5 atom % D
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥99% (CP)
Forme
solution
Contient
0.03 % (v/v) TMS
Technique(s)
NMR: suitable
Impuretés
≤0.05% water
water
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.428 (lit.)
pb
153 °C (lit.)
Densité
1.03 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Changement de masse
M+7
Chaîne SMILES
[2H]C(=O)N(C([2H])([2H])[2H])C([2H])([2H])[2H]
InChI
1S/C3H7NO/c1-4(2)3-5/h3H,1-2H3/i1D3,2D3,3D
Clé InChI
ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-YYWVXINBSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Produits recommandés
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Repr. 1B
Code de la classe de stockage
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
136.4 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
58 °C - closed cup
Listes réglementaires
Les listes réglementaires sont principalement fournies pour les produits chimiques. Seules des informations limitées peuvent être fournies ici pour les produits non chimiques. L'absence d'indication signifie qu'aucun des composants n'est répertorié. Il incombe à l'utilisateur de s'assurer de l'utilisation sûre et légale du produit.
EU REACH SVHC Candidate List
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique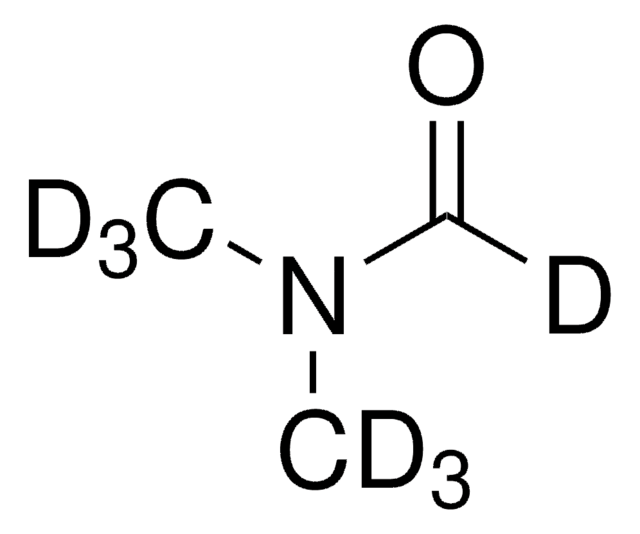


![(3R)-3-{[(9H-Fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}-3-(3-methylphenyl)propanoic acid AldrichCPR](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/369/030/c37536c8-fce7-456d-a3f2-1b29a57c2c52/640/c37536c8-fce7-456d-a3f2-1b29a57c2c52.png)