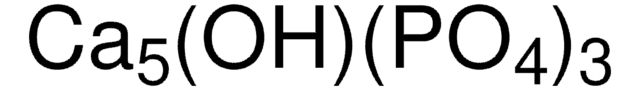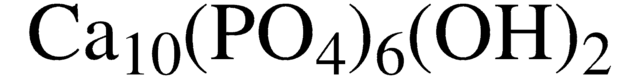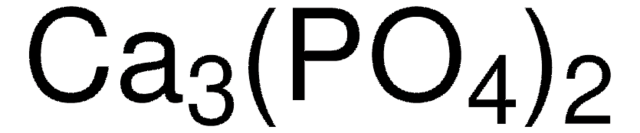677418
Hydroxyapatite
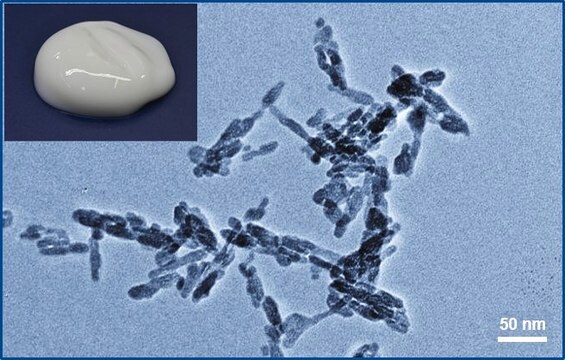
nanopowder, <200 nm particle size (BET), ≥97%, synthetic
Synonyme(s) :
Calcium hydroxyphosphate, HAp, Hydroxylapatite
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
≥97%
Forme
nanopowder
solid
Superficie
>9.4 m2/g
Taille des particules
<200 nm (BET)
Pf
1100 °C (lit.)
Chaîne SMILES
[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].O[Ca+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/5Ca.3H3O4P.H2O/c;;;;;3*1-5(2,3)4;/h;;;;;3*(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2/q5*+2;;;;/p-10
Clé InChI
XYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-D
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
Poly (sodium 4-styrene sulfonate)-modified hydroxyapatite nanoparticles can be used as a drug carrier for vancomycin. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles control the release of antibiotics after the implantation of a scaffold in the body.
Porous hydroxyapatite microspheres exhibit a high adsorptive capacity for heavy metals and can be used for the treatment of heavy metal contaminated water.
Caractéristiques et avantages
- Bioactive and biocompatible
- Good mechanical strength
- Porous structure
- Osteoconductive and osteointegrative properties
Informations légales
Code de la classe de stockage
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique