32598
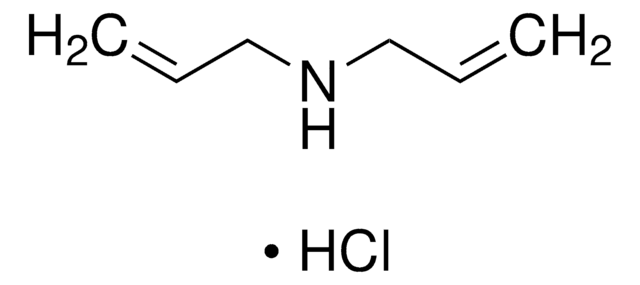
Diallyldimethylammonium chloride
≥97.0% (AT)
Synonyme(s) :
DADMAC, Dimethyldiallylammonium chloride, N,N-Diallyl-N,N-dimethylammonium chloride
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
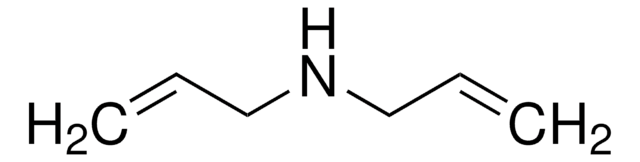
Formule linéaire :
(CH2=CHCH2)2N(Cl)(CH3)2
Numéro CAS:
Poids moléculaire :
161.67
Beilstein:
5830817
Numéro CE :
Numéro MDL:
Code UNSPSC :
12162002
ID de substance PubChem :
Nomenclature NACRES :
NA.23
Produits recommandés
Essai
≥97.0% (AT)
Forme
solid
Pf
140-148 °C
Chaîne SMILES
[Cl-].C[N+](C)(CC=C)CC=C
InChI
1S/C8H16N.ClH/c1-5-7-9(3,4)8-6-2;/h5-6H,1-2,7-8H2,3-4H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
Clé InChI
GQOKIYDTHHZSCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Description générale
Diallyldimethylammonium chloride (DADMAC) is a quaternary ammonium compound available in solid form with an assay of ≥97.0%. It serves as a versatile monomer in various polymerization processes and is primarily used in the production of cationic polymers. These polymers are essential in a range of applications, particularly in the fields of water treatment, paper production, and personal care products. Additionally, DADMAC exhibits antifouling properties, making it valuable for applications where the prevention of biofilm formation and surface fouling is critical.
Application
Diallyldimethylammonium chloride can be used as:
- A precursor for the synthesis of poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC), which is widely used in various applications related to water purification and wastewater management.
- a monomer in the synthesis of cationic hydrogels via radical polymerization. The resulting polymer, poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC), features a high cationic charge density, which is crucial for effectively binding anionic dyes. This property makes PDADMAC-based hydrogels valuable materials for wastewater treatment applications.
- DADMAC has been used in dental biomaterials to enhance their antifouling properties. When incorporated into acrylic resins, it provides effective antibacterial and antifungal activity without compromising biocompatibility
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Yuanyuan Zhang et al.
ACS nano, 9(7), 7124-7132 (2015-07-15)
In this study, we demonstrate multilevel and multicomponent layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly as a convenient and generally applicable method for the fabrication of nanofibrillar films by exploiting the dynamic nature of polymeric complexes. The alternate deposition of poly(allylamine hydrochloride)-methyl red (PAH-MR)
Deyi Zhu et al.
Journal of industrial microbiology & biotechnology, 42(2), 189-196 (2014-12-30)
Collagen fiber (CF), an abundant natural biopolymer, features many favorable properties that make it a potential carrier for cell immobilization. In the present investigation, CF was grafted with polyethyleneimine (PEI) using glutaraldehyde (GA) as the cross-linking agent, resulting in the
Zhenxi Zhang et al.
Journal of biomedical optics, 20(5), 51043-51043 (2015-05-30)
There are three possible mechanisms for 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) conjugated gold nanoparticles (GNPs) through electrostatic bonding for photodynamic therapy (PDT) of cancer: GNPs delivery function,singlet oxygen generation (SOG) by GNPs irradiated by light, and surface resonance enhancement (SRE) of SOG.
Ya Xiong et al.
Talanta, 129, 282-289 (2014-08-17)
Simple, rapid and sensitive analysis of thrombin (a tumor biomarker) in complex samples is quite clinical relevant and essential for the development of disease diagnosis and pharmacotherapy. Herein, we developed a novel method based on aptamer-conjugated magnetic graphene/gold nanoparticles nanocomposites
Feng Gu et al.
Journal of chromatography. A, 1376, 53-63 (2014-12-30)
The main objective of our research was to develop silica-based, polymer-functionalized ion exchange materials for single-use bioprocess applications, with the ultimate goal of achieving maximal binding capacity for target proteins. Herein we report the utilization of Grace(®) wide pore silica
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique

![[2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution 75 wt. % in H2O](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/316/612/66b0f4cf-d060-427d-b4f5-e8fab3e5cffe/640/66b0f4cf-d060-427d-b4f5-e8fab3e5cffe.png)
![[2-(Acryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution 80 wt. % in H2O, contains 600 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/393/326/f7e19585-5431-4220-81b5-f458de6d63d0/640/f7e19585-5431-4220-81b5-f458de6d63d0.png)