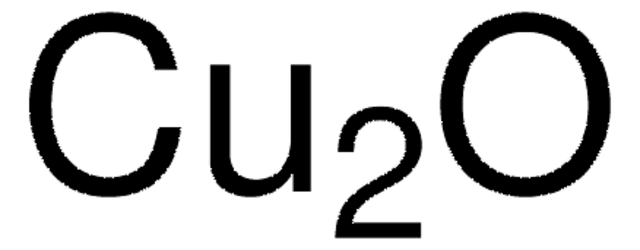229628
Copper(I) chloride
≥99.995% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
Copper monochloride, Cuprous chloride
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
for analytical purposes
Niveau de qualité
Pression de vapeur
1.3 mmHg ( 546 °C)
Essai
≥99.995% trace metals basis
Forme
powder
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: catalyst
core: copper
Technique(s)
mass spectrometry (MS): suitable
Impuretés
≤50.0 ppm Trace Rare Earth Analysis
pb
1490 °C (lit.)
Pf
430 °C (lit.)
Solubilité
slightly soluble 0.47 g/L at 20 °C
Application(s)
battery manufacturing
Chaîne SMILES
Cl[Cu]
InChI
1S/ClH.Cu/h1H;/q;+1/p-1
Clé InChI
OXBLHERUFWYNTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
Shows unique character as an initiator of radical reactions such as the hydrostannation of α,β-unsaturated ketones.
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Oxidation and reduction reactions are some of the most common transformations encountered in organic synthesis
Thermoelectric Performance of Perovskite-type Oxide Materials
Spectral conversion for solar cells is an emerging concept in the field of photovoltaics, and it has the potential to increase significantly the efficiency of solar cells. Lanthanide ions are ideal candidates for spectral conversion, due to their high luminescence efficiencies and rich energy level structure that allows for great flexibility in the upconversion and downconversion of photons in a wide spectral region (NIR-VIS-UV).
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Protocoles
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Global Trade Item Number
| Référence | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 229628-100G | 4061833595718 |
| 229628-10G | 4061838781963 |
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique