53604
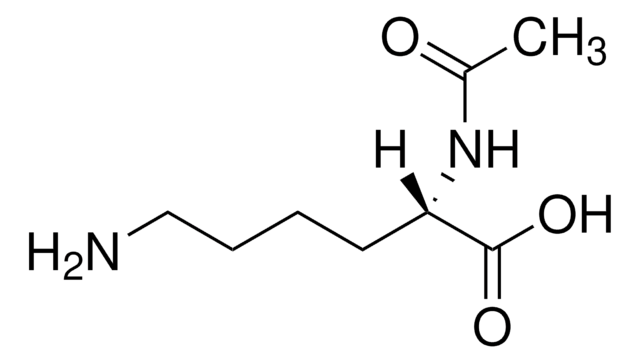
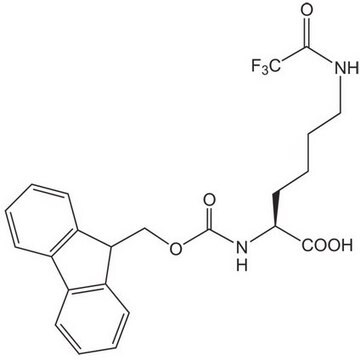
Nε-Trifluoroacetyl-L-lysine
≥96.0% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
ε-TFA-lysine
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C8H13F3N2O3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
242.20
Beilstein:
2122429
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥96.0% (TLC)
form
powder
impurities
≤7% water
color
white to off-white
mp
>215 °C
solubility
2 M HCl: 10 mg/mL, clear, colorless
application(s)
peptide synthesis
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
N[C@@H](CCCCNC(=O)C(F)(F)F)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C8H13F3N2O3/c9-8(10,11)7(16)13-4-2-1-3-5(12)6(14)15/h5H,1-4,12H2,(H,13,16)(H,14,15)/t5-/m0/s1
InChI key
PZZHRSVBHRVIMI-YFKPBYRVSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nε-Trifluoroacetyl-L-lysine is an inhibitor of L-lysine cyclodeaminase.
Nε-Trifluoroacetyl-L-lysine may be used to create synthetic organic polypeptides useful for nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Georgia Eleni Tsotsou et al.
Biochimie, 89(5), 591-604 (2007-02-13)
L-Lysine cyclodeaminase from Streptomyces pristinaespiralis was heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli, isolated to 90% purity after two purification steps and characterised. The size of the isolated recombinant enzyme was in agreement with the theoretical size calculated from the corresponding gene.
Gerhard K E Scriba
Journal of chromatography. A, 1159(1-2), 28-41 (2007-02-24)
Nonaqueous background electrolytes broaden the application of capillary electrophoresis displaying altered separation selectivity and interactions between analytes and buffer additives compared to aqueous background electrolytes. In addition, nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) appears to be ideally suited for online coupling with
Hervé Cottet et al.
Analytical chemistry, 75(20), 5554-5560 (2004-01-09)
Poly(Nepsilon-trifluoroacetyl-L-lysine) was used as a model solute to investigate the potential of nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) for the characterization of synthetic organic polymers. The information obtained by NACE was compared to that derived from size exclusion chromatography (SEC) experiments, and
Laurent Geiser et al.
Electrophoresis, 30(1), 36-49 (2008-12-25)
This review article presents recent developments and applications of non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE): The text covers the period from the previous review (L. Geiser, J. L. Veuthey, Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 45-57) to summer 2008. We focus primarily on the analysis
S M Furst et al.
International archives of allergy and immunology, 114(1), 46-53 (1997-09-26)
The purpose of this study was to investigate lymphocyte adhesion to Kupffer cells as a component of an immune-mediated mechanism for halothane hepatitis. Kupffer cells were isolated from guinea pigs exposed to 1.0% halothane/40% oxygen and cultured with various synthetic
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service