T6632
Thymidine Phosphorylase, recombinant from Escherichia coli
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution, ≥900 units/mL, 0.2 μm filtered
Synonym(s):
Thymidine:orthophosphate deoxy-D-ribosyltransferase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
sterility
0.2 μm filtered
form
buffered aqueous solution
concentration
≥900 units/mL
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
Escherichia coli K12 ... deoA(948901)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Thymidine phosphorylase inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.
Application
Thymidine phosphorylase has been used in a study to evaluate biomarkers for advanced breast cancer patients treated with capecitabine-based first-line chemotherapy. Thymidine phosphorylase has also been used in a study to investigate implications for the clinical efficacy of nucleoside analogues.
Biochem/physiol Actions
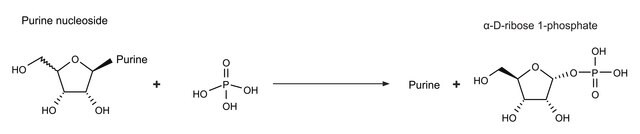
An enzyme that catalyzes the reversible conversion of thymidine to thymine. Thymidine phosphorylase is part of the pyrimidine nucleoside salvage pathway.
An enzyme that catalyzes the reversible conversion of thymidine to thymine. Thymidine phosphorylase is part of the pyrimidine nucleoside salvage pathway. This pathway allows pyrimidine bases to be recycled for nucleotide biosynthesis, while the pentose 1-phosphates are converted to intermediates of the pentose phosphate shunt and glycolysis. The E. coli thymidine phosphorylase shares 40% sequence homology with the human sequence, which has been found to be identical to the angiogenic agent platelet-derived endothelial growth factor. The purified E. coli enzyme has been shown to stimulate blood vessel growth in chick chorioallantoic membrane assays.
Unit Definition
One unit will convert 1.0 μmole each of thymidine and phosphate to thymine and 2-deoxyribose 1-phosphate per min at pH 7.4 at 25°C.
Physical form
Solution in 0.5 M potassium phosphate containing 2 mM uracil, 0.02% sodium azide and bovine serum albumin
Preparation Note
Cloned from E. coli and produced in overexpressing E. coli
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Domenico Ribatti et al.
Expert opinion on therapeutic targets, 16(12), 1215-1225 (2012-09-18)
Several anti-angiogenic agents have been developed and some of them have been clinically applied in the tumor therapy. Anti-angiogenic therapy faces some hurdles: inherent or acquired resistance, increased invasiveness, and lack of biomarkers. Characterization of tumor endothelial markers may help
Richard A Norman et al.
Structure (London, England : 1993), 12(1), 75-84 (2004-01-17)
Human thymidine phosphorylase (HTP), also known as platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor (PD-ECGF), is overexpressed in certain solid tumors where it is linked to poor prognosis. HTP expression is utilized for certain chemotherapeutic strategies and is also thought to play
Alexandra Giatromanolaki et al.
Cancer biology & therapy, 13(13), 1284-1289 (2012-08-17)
Tumor-associated stroma (TAS) is not simply a supporting element for cancer cells, but plays an important role in tumor growth, invasion and metastasis. Changes on the level of stromal constituents, such as loss of Caveolin-1 and increased thymidine phosphorylase (TP)
Hong-Yun Zhao et al.
Anti-cancer drugs, 23(5), 534-542 (2012-04-07)
The aim of the present study was to investigate the gene expression of biomarkers associated with the sensitivity to fluoropyrimidine and taxanes in recurrent/advanced breast cancer patients treated with first-line capecitabine chemotherapy. We evaluated the clinicopathological/prognostic significance of thymidylate synthase
Michelle Levene et al.
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology, 131(1), 311-324 (2012-09-15)
Erythrocyte-encapsulated thymidine phosphorylase (EE-TP) is currently under development as an enzyme replacement therapy for mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalomyopathy (MNGIE), an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency of thymidine phosphorylase. The rationale for the development of EE-TP is based on the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service