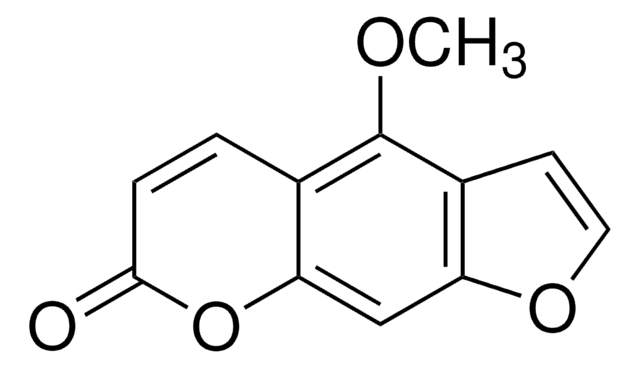
P8399
Psoralen
≥99% (HPLC)
Synonym(s):
6,7-Furanocoumarin, 7H-Furo[3,2-g]benzopyran-7-one, Ficusin, Furo[3,2-g]coumarin
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99% (HPLC)
form
powder
fluorescence
λex 335 nm; λem 460 nm (pH 7.0)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
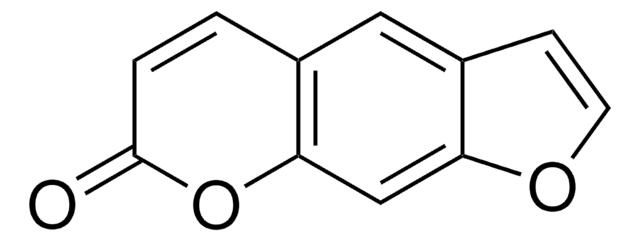
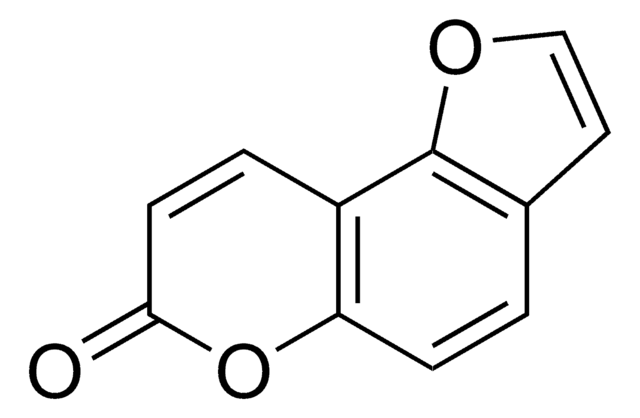
O=C1Oc2cc3occc3cc2C=C1
InChI
1S/C11H6O3/c12-11-2-1-7-5-8-3-4-13-9(8)6-10(7)14-11/h1-6H
InChI key
ZCCUUQDIBDJBTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- as a crosslinker for dsRNA for in- situ hybridization studies
- in testing melanin dispersal effects in fish scale melanophores
- to test its stimulatory effects in osteoblast a cell proliferation assay
- as a reference standard in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
DNA damage and repair mechanism is vital for maintaining DNA integrity. Damage to cellular DNA is involved in mutagenesis, the development of cancer among others.
n proliferating cells, the cell cycle consists of four phases. Gap 1 (G1) is the interval between mitosis and DNA replication that is characterized by cell growth. Replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis (S) phase, which is followed by a second gap phase (G2) during which growth and preparation for cell division occurs. Together, these three stages comprise the interphase phase of the cell cycle. Interphase is followed by the mitotic (M) phase.
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is a selective process for the removal of unnecessary, infected or transformed cells in various biological systems. As it plays a role in the homeostasis of multicellular organisms, apoptosis is tightly regulated through two principal pathways by a number of regulatory and effector molecules.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service