G8761
(±)-Gossypol from cotton seeds
≥95% (HPLC), powder, PAF antagonist/inhibitor
Synonym(s):
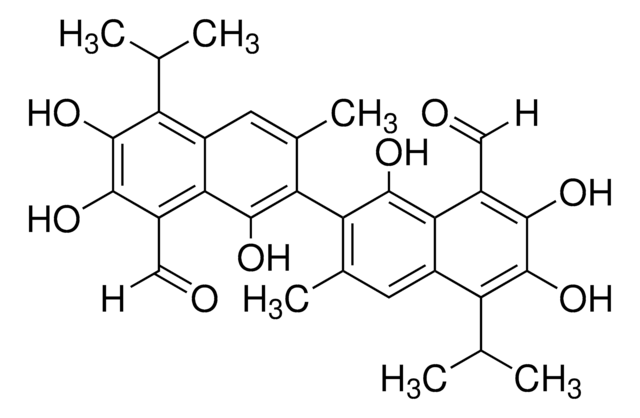
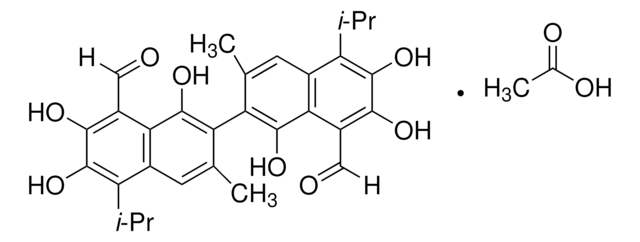
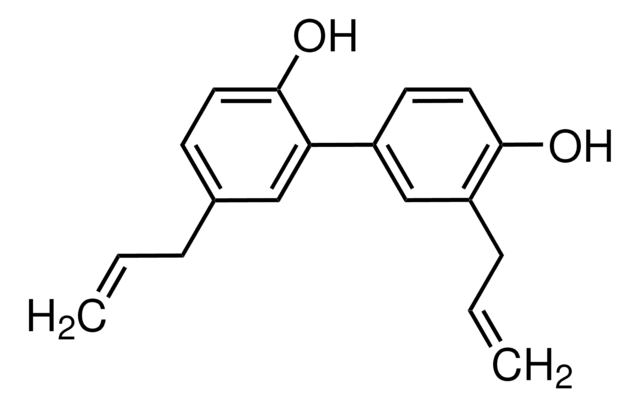
(±)-2,2′-bis(8-Formyl-1,6,7-trihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-methylnaphthalene)
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
(±)-Gossypol from cotton seeds, ≥95% (HPLC)
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O=C([H])C1=C(C(O)=C(C2=C(C)C=C(C(C(C)C)=C(O)C(O)=C3C([H])=O)C3=C2O)C(C)=C4)C4=C(C(C)C)C(O)=C1O
InChI
1S/C30H30O8/c1-11(2)19-15-7-13(5)21(27(35)23(15)17(9-31)25(33)29(19)37)22-14(6)8-16-20(12(3)4)30(38)26(34)18(10-32)24(16)28(22)36/h7-12,33-38H,1-6H3
InChI key
QBKSWRVVCFFDOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... AKR1B1(231) , BAD(572) , BCL2(596) , LDHA(3939) , LDHB(3945) , MCL1(4170)
General description
Application
- as a standard to quantify the gossypol content in the extracts of leaves and flower buds
- to study its antifertility effects on spermatogenesis in NMRI mice
- to analyse its impact on human spermatozoa
- to incorporate into the artificial diet for larval rearing
Biochem/physiol Actions
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Repr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
We presents an article about the Warburg effect, and how it is the enhanced conversion of glucose to lactate observed in tumor cells, even in the presence of normal levels of oxygen. Otto Heinrich Warburg demonstrated in 1924 that cancer cells show an increased dependence on glycolysis to meet their energy needs, regardless of whether they were well-oxygenated or not.
Related Content
DISCOVER Bioactive Small Molecules for Nitric Oxide & Cell Stress Research
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service