ECM002
Thrombospondin-1 human
recombinant, expressed in HEK 293 cells, lyophilized powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
THBS, THBS1, TSP, TSP1, Thrombospondin-1
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in HEK 293 cells
sterility
sterile
Assay
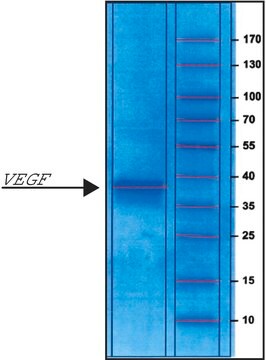
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
mol wt
127.5 kDa (The protein migrates as a 140 kDa band on SDS-PAGE due to glycosylation.)
packaging
pkg of 50 μg
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
≤1 EU/μg endotoxin, tested
solubility
water: soluble
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... THBS1(7057)
General description
Application
- To treat hepatocyte (IHH) cancer cells to study the role of aspartyl protease 1 (MfSAP1) in extracellular matrix degradation.
- In in vitro Extracellular Matrix (ECM) protein degradation assays.
- In rat C6 astroglioma cells, for coating the cell culture plates to study the effects of integrins on CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) expression.
- In the preparation of secreted factor cocktail for analysis of the human mesenchymal stem cell secretome.
Recommended for use as a cell culture substratum at 1-5 μg/cm2 or 0.1-25 μg/ml. Optimal concentration depends on cell type as well as the application or research objectives.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
- Human-derived thrombospondin
- Produced through recombinant expression in HEK 293 cells
- Low endotoxin levels
Physical form
Analysis Note
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
The extracellular matrix (ECM) and its attachment factor components are discussed in this article in relation to their function in structural biology and their availability for in vitro applications.
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is secreted by cells and surrounds them in tissues.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service