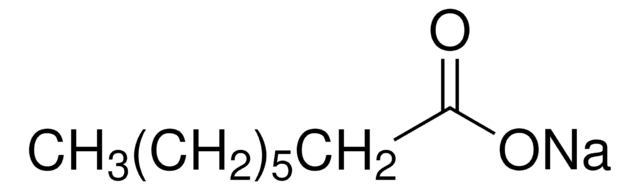C4151
Sodium decanoate
≥98%
Synonym(s):
Capric acid sodium salt, Decanoic acid sodium salt, Sodium caprate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3(CH2)8COONa
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
194.25
Beilstein:
3572742
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352211
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
biological source
natural (organic)
Quality Level
Assay
≥98%
form
powder
functional group
ester
lipid type
saturated FAs
shipped in
ambient
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[Na+].CCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C10H20O2.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10(11)12;/h2-9H2,1H3,(H,11,12);/q;+1/p-1
InChI key
FIWQZURFGYXCEO-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- Neonatal intestinal mucus barrier changes in response to maturity, inflammation, and sodium decanoate supplementation.: This study elucidates how sodium decanoate affects neonatal intestinal barriers, indicating its potential for nutritional interventions to enhance mucosal immunity and gastrointestinal health (Ronholt et al., 2024).
- Effects of Sodium Salts of Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives on Skin Permeation of Cromolyn Sodium.: Demonstrates the role of sodium decanoate in enhancing skin permeability, offering insights into its applications in transdermal drug delivery systems (Dinh et al., 2023).
- The Role of Paracellular Transport in the Intestinal Absorption and Biopharmaceutical Characterization of Minoxidil.: Highlights sodium decanoate′s impact on the intestinal absorption mechanisms, contributing to the development of more effective oral drug formulations (Dahan et al., 2022).
- Control of Escherichia coli Serotype O157:H7 Motility and Biofilm Formation by Salicylate and Decanoate: MarA/SoxS/Rob and pchE Interactions.: Investigates how sodium decanoate influences bacterial behavior, particularly in managing pathogenicity and biofilm control, which is crucial for both clinical and environmental applications (Ream et al., 2022).
- Sodium Decanoate Improves Intestinal Epithelial Barrier and Antioxidation via Activating G Protein-Coupled Receptor-43.: This research explores sodium decanoate′s therapeutic potential in strengthening intestinal barriers and enhancing antioxidative properties, making it a candidate for gastroenterological treatments (Ma et al., 2021).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Ignacio Poblete-Castro et al.
Microbial cell factories, 11, 34-34 (2012-03-22)
Pseudomonas putida KT2442 is a natural producer of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), which can substitute petroleum-based non-renewable plastics and form the basis for the production of tailor-made biopolymers. However, despite the substantial body of work on PHA production by P. putida strains
C Roos et al.
European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics : official journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik e.V, 142, 387-395 (2019-07-16)
Oral administration of drug products is the preferred administration route. In recent decades there has been an increase in drug candidates with low solubility and/or low permeability. To increase the possibility of oral administration for the poorly permeating drugs, the
Ahmed Kassem et al.
International journal of food microbiology, 261, 19-24 (2017-09-11)
The aim of the current study was to assess the ability of a number of chemicals (acetic Acid (AA), citric acid (CA) lactic acid (LA), sodium decanoate (SD) and trisodium phosphate (TSP)) to reduce microbial populations (total viable count, Campylobacter
D Dahlgren et al.
International journal of pharmaceutics, 549(1-2), 239-248 (2018-07-29)
The small intestine mucosal barrier is physiologically regulated by the luminal conditions, where intestinal factors, such as diet and luminal tonicity, can affect mucosal permeability. The intestinal barrier may also be affected by absorption-modifying excipients (AME) in oral drug delivery
Wei Li et al.
Otology & neurotology : official publication of the American Otological Society, American Neurotology Society [and] European Academy of Otology and Neurotology, 39(5), 639-647 (2018-04-13)
Entry of locally applied drugs into the inner ear can be enhanced by chemical manipulations. Perilymph drug concentrations achieved by intratympanic applications are well below the applied concentration due to limited entry through the round window (RW) membrane and stapes.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service