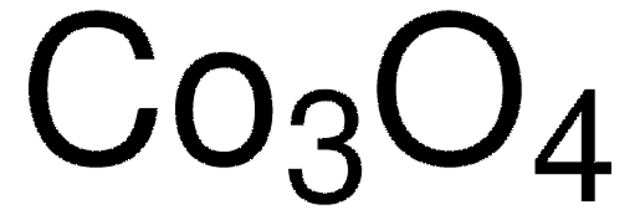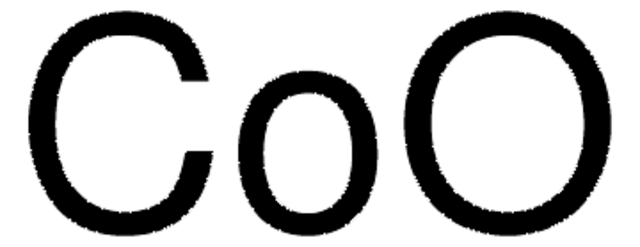637130
Nickel(II) oxide
nanopowder, <50 nm particle size (TEM), 99.8% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Nickel monooxide, Nickelous oxide
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99.8% trace metals basis
form
nanopowder
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
color
green to black
particle size
<50 nm (TEM)
density
6.67 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
bulk density
0.51 g/mL
application(s)
battery manufacturing
greener alternative category
SMILES string
[Ni]=O
InChI
1S/Ni.O
InChI key
GNRSAWUEBMWBQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 4 - Carc. 1A Inhalation - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Target Organs
Lungs
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Currently, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are attracting a lot of attention because of the possibility of many novel applications, especially in biomedical research.
Mechanical alloying is a “brute force” method of affecting alloying and chemical reactions. The mixture of reactant powders and several balls are placed in the milling jar of a high-energy ball mill, for example, a shaker mill or a planetary mill.
As with all types of fuel cells, a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) is capable of efficiently transforming chemical energy into electrical energy.
The application of magnetism and magnetic materials pervades our modern civilization in the form of electrical power, communications and information storage.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 637130-250G | 4061832723709 |
| 637130-100G | 4061838820556 |
| 637130-25G | 4061832723808 |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service