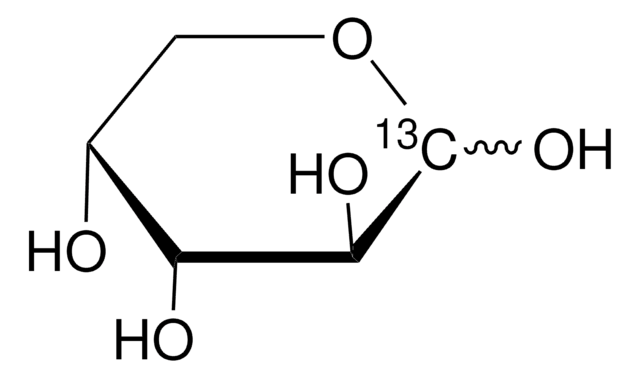
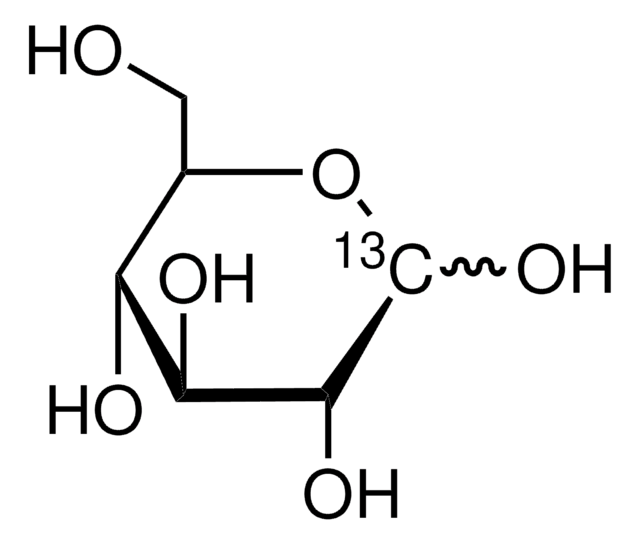
About This Item
Recommended Products
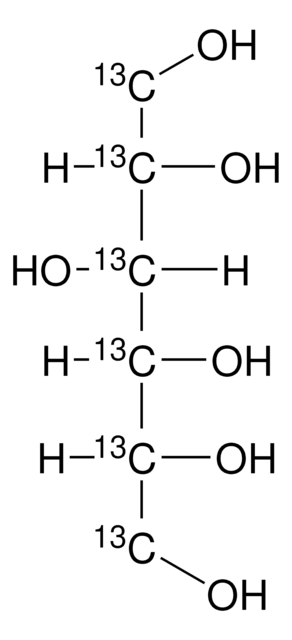
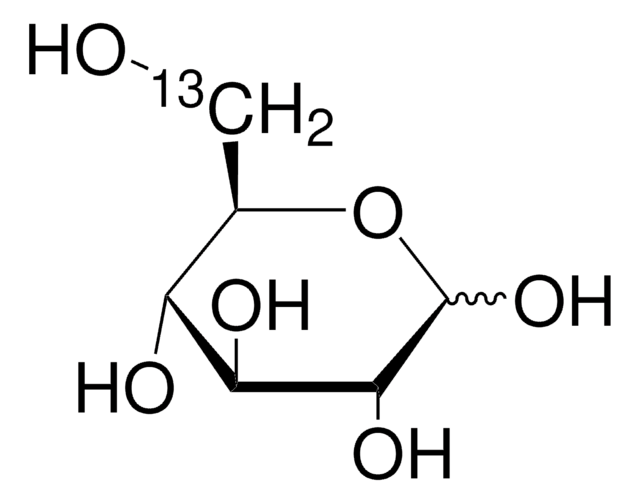
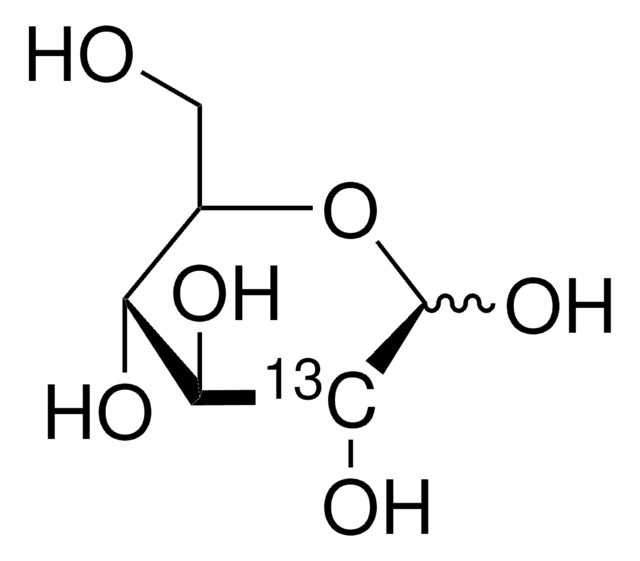
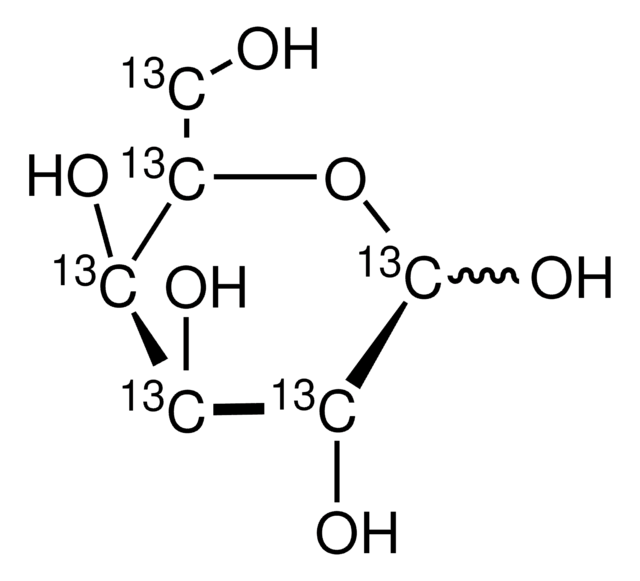
isotopic purity
99 atom % 13C
Assay
≥99% (HPLC)
form
powder
optical activity
[α]25/D +79.0, c = 2 in H2O (trace NH4OH)
mp
169-170 °C (lit.)
mass shift
M+1
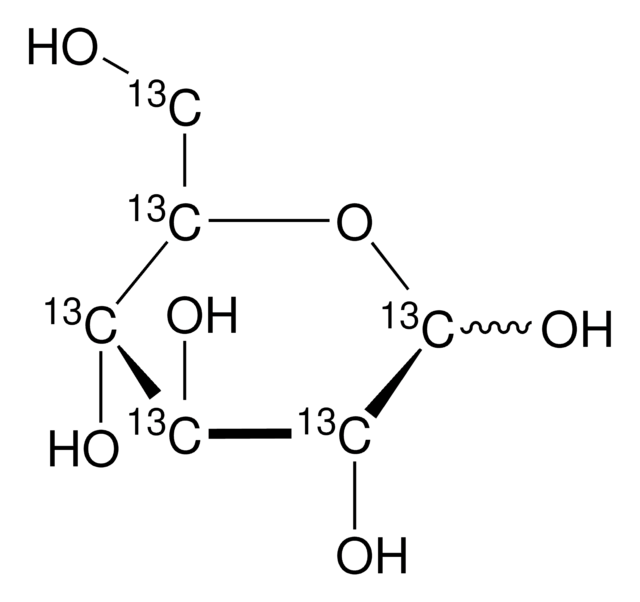
SMILES string
OC[C@H]1O[13CH](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O
InChI
1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3+,4+,5-,6?/m1/s1/i6+1
InChI key
WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-ZGYLHYIGSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Packaging
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (DNP) is a phenomenon by which high spin polarization, typically derived from a bath of free radical electrons, is transferred to a nuclear spin bath, enhancing the difference between the nuclear energy levels and thereby producing dramatically enhanced NMR signals for detection.
Sigma-Aldrich.com presents an article concerning MRI/MRS and the use of isotopes in hyperpolarization.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service