Allgemeine Beschreibung
Dystrophin is a muscle membrane protein (427 kDa) which is absent, reduced or altered as a result of mutation in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies (DMD/BMD) or its homologue in the mouse. Severe DMD is associated with a marked dystrophin deficiency whereas patients with the milder form of DMD show less pronounced abnormalities of protein expression. Because abnormalities in the protein expression occur specifically in patients with these types of muscular dystrophy, dystrophin analysis may be used to distinguish these conditions from other neuromuscular diseases. Predictions from the sequence suggest a structural protein on the inner face of the membrane, consisting of a 25-repeat, rod-like triple-helical domain separating an N-terminal actin-binding domain from two C-terminal domains, one of which is rich in cysteine. The large size of dystrophin and its low abundance (<0.01% of the total muscle protein) are a hindrance to the isolation of intact, native protein for structure/function studies.
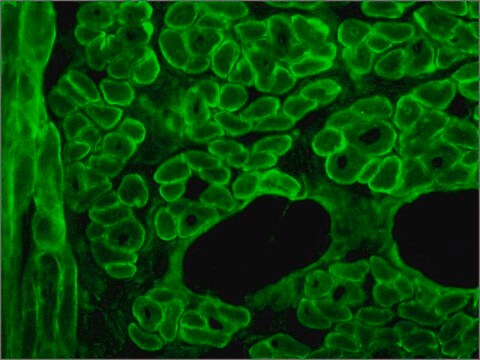
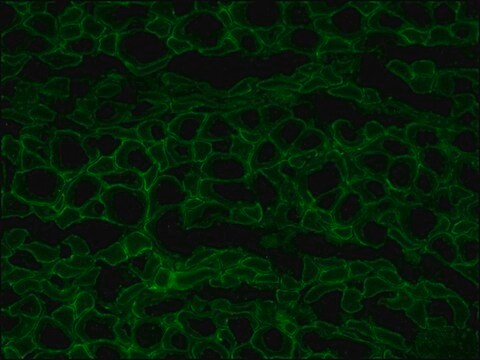
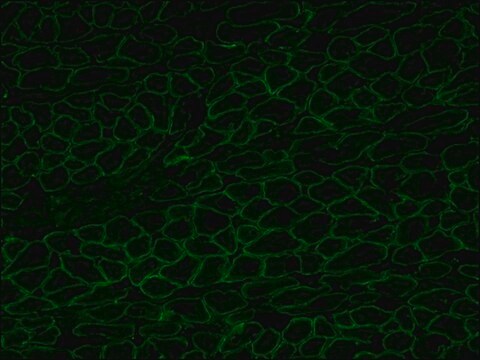
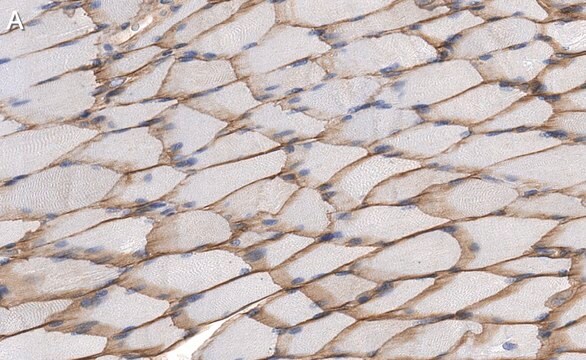
The antibody recognizes an epitope located on the 128 amino acids at the end of the C-terminal domain of the human dystrophin molecule (amino acid residues 3558-3684). Immunohistochemical staining of muscle tissue results in a clear labeling confined to the periphery (plasma membrane) of normal striated muscle fibers. By immunoblotting, the antibody stains dystrophin (427 kDa) in muscle and brain extracts. It also stains the 70-75 kDa protein known as Apo-Dystrophin-1 or Dp71.4 This is detected in the brain as well as in lymphoblastoid cells, cultures of brain astroglial and neuronal cells, liver and Hep G2 cells (human hepatoma). The epitope recognized by the antibody is sensitive to formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. The antibody exhibits a wide interspecies cross-reactivity. It is useful in ELISA and capture ELISA. The antibody is specific to dystrophin and does not react with α-actinin and utrophin, an autosomal homologue of dystrophin, also called dystrophin-related protein (DRP).
Spezifität
The antibody recognizes an epitope located on the 128 amino acids at the end of the C-terminal domain of the human dystrophin molecule (amino acid residues 3558-3684). Immunohistochemical staining of muscle tissue results in a clear labeling confined to the periphery (plasma membrane) of normal striated muscle fibers. By immunoblotting, the antibody stains dystrophin (427 kDa) in muscle and brain extracts. It also stains the 70-75 kDa protein known as Apo-Dystrophin-1 or Dp71.4 This is detected in the brain as well as in lymphoblastoid cells, cultures of brain astroglial and neuronal cells, liver and Hep G2 cells (human hepatoma). The epitope recognized by the antibody is sensitive to formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. The antibody exhibits a wide interspecies cross-reactivity. It is useful in ELISA and capture ELISA. The antibody is specific to dystrophin and does not react with α-actinin and utrophin, an autosomal homologue of dystrophin, also called dystrophin-related protein (DRP).
Immunogen
fusion protein containing the C-terminal amino acids of human dystrophine.
Anwendung
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Immunofluorescence (1 paper)Western Blotting (1 paper)Mouse monoclonal clone MANDRA1 anti-Dystrophin antibody may be used for the localization of dystrophin using various immunochemical assays such as ELISA, capture ELISA, immunoblot, and immunohistochemistry. Monoclonal antibodies against defined regions of dystrophin provide a means for studying its structure and function, interactions with other proteins and the nature of the partial gene products produced in some patients carrying deletions in the dystrophin gene. The antibodies are useful in the prenatal or post-abortion diagnosis of muscular dystrophy carriers by immunohistological analyses.
Zielbeschreibung
The C-terminal domain of the human dystrophin molecule (amino acids residues 3558-3684) is present in normal muscle tissue. It is also present in nearly all Becker muscular dystrophies, but is absent in cases of Duchenne muscular dystrophies and in the dystrophic mouse (mdx).
Haftungsausschluss
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.