Wichtige Dokumente
B6650
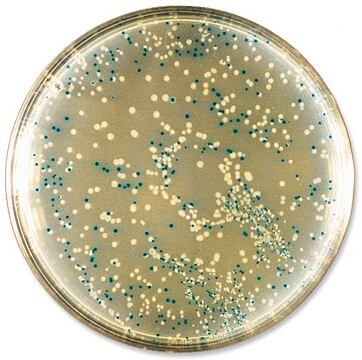
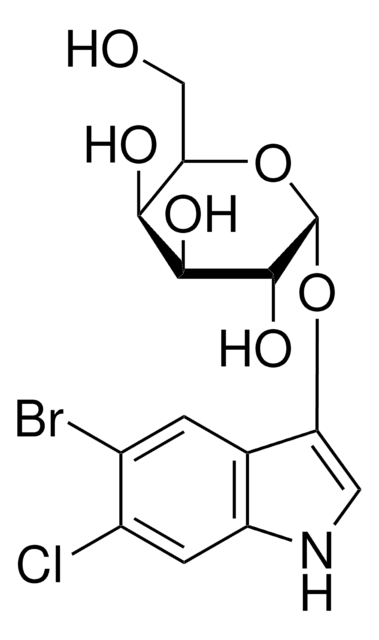
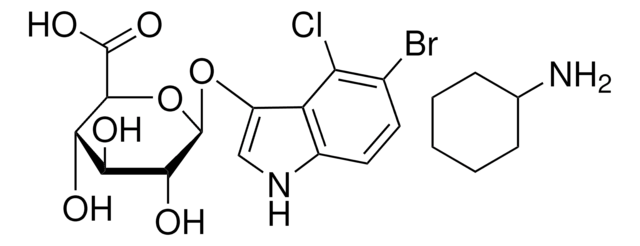
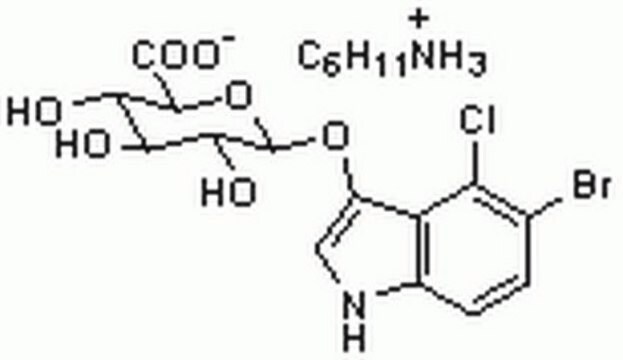
X-GlcA
reagent for selection of recombinant bacterial clones
Synonym(e):
5-Brom-4-Chlor-3-Indolyl β-D-Glucuronid Cyclohexylaminsalz, X-GlcA, X-glucuronid Cyclohexylaminsalz
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualität
for molecular biology
Sterilität
non-sterile
Assay
≥98% (TLC)
Form
powder
Methode(n)
nucleic acid detection: suitable
Löslichkeit
DMF: soluble
Eignung
suitable for β-galactosidase test
Lagertemp.
−20°C
SMILES String
NC1CCCCC1.O[C@@H]2[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]([C@H]2O)C(O)=O)Oc3c[nH]c4ccc(Br)c(Cl)c34
InChI
1S/C14H13BrClNO7.C6H13N/c15-4-1-2-5-7(8(4)16)6(3-17-5)23-14-11(20)9(18)10(19)12(24-14)13(21)22;7-6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h1-3,9-12,14,17-20H,(H,21,22);6H,1-5,7H2/t9-,10-,11+,12-,14+;/m0./s1
InChIKey
JXCKZXHCJOVIAV-CYRSAHDMSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
X-GlcA has been used in histochemical staining of root sections for light microscopic observation.
Prinzip
Ähnliches Produkt
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Today, diverse studies report the benefits of probiotics, such as inhibitory effects on pathogens, aid in the management or prevention of chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases or atopic syndromes, and support to the immune system. Potential beneficial applications abound, researchers continue to evaluate the effictiveness and clarify the mechanisms of action of probiotics.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.