HAWP01300
MCE-Membranfilter, Porengröße 0,45 μm
MF-Millipore™, filter diam. 13 mm, hydrophilic, white
Synonym(e):
MF-Millipore™ Membrane Filter, 0.45 µm pore size
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Materialien
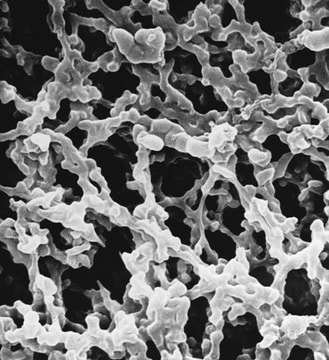
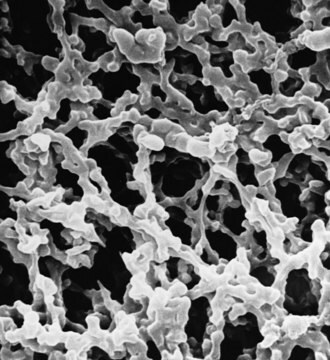
mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane
plain filter
white filter
Qualitätsniveau
Beschreibung
13 mm diameter, mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, hydrophilic, white, 100 discs
Sterilität
non-sterile
Leistungsmerkmale
hydrophilic
Hersteller/Markenname
MF-Millipore™
Millipore
Parameter
4 L/min-cm2 air flow rate
60 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate
75 °C max. temp.
Durchmesser
13 mm
Filterdurchm.
13 mm
Dicke
150 μm
Gravimetrisch bestimmte extrahierbare Substanzen
2.5%
Farbe
white
Brechungsindex
n/D 1.51
Matrix
MF-Millipore™
Porengröße
0.45 μm pore size
79 % porosity
Kapazität
150 μg/cm2 binding capacity (protein)
160 μg/cm2 adsorption capacity (insulin)
Blasenpunkt
≥1.8 bar, air with water at 23 °C
Versandbedingung
ambient
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
MF-Millipore filters without Triton surfactant contain minimum amounts of wetting agent and have a lower water extractable content than standard MF-Millipore filters.
Features & Benefits:
- Versatile filter for biological and environmental monitoring applications
- Available in a range of pore sizes, colored black or white, with or without a gridded surface
- Compatible with ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation, and autoclave sterilization methods
Anwendung
- Clarification of aqueous solutions
- Particle removal
- Particle analysis
- Microbiology analysis
- Isolation of virus-like particles in wastewater
- Microplastics analysis grade water
- Nucleic acid binding, including eDNA
Sonstige Hinweise
- Organism Retention: Microorganism
- Mode of Action: Filtration (size exclusion)
- Application: General laboratory filtration
- Intended Use: Retention or removal of biological contaminants
- Instructions for Use: Sterilizing filtration of a liquid through a membrane with a 0.2 μm (or smaller) pore size effectively removes biological contaminants, including bacteria, mold and yeast. For the selective retention of larger biological contaminents, liquid filtration through membranes with 0.45 μm (or larger) pore sizes may be used to trap and support microorganism growth for subsequent culture and analysis
- Storage Statement: Store in dry location away from heat source
- Disposal Statement: Dispose of in accordance with applicable federal, state and local regulations.
Rechtliche Hinweise
Signalwort
Danger
H-Sätze
Gefahreneinstufungen
Flam. Sol. 1
Lagerklassenschlüssel
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Zulassungslistungen
Zulassungslistungen werden hauptsächlich für chemische Produkte erstellt. Für nicht-chemische Produkte können hier nur begrenzte Angaben gemacht werden. Kein Eintrag bedeutet, dass keine der Komponenten gelistet ist. Es liegt in der Verantwortung des Benutzers, die sichere und legale Verwendung des Produkts zu gewährleisten.
EU REACH SVHC Candidate List
EU REACH Annex XIV (Authorisation List)
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.