Alle Fotos(2)
Wichtige Dokumente
857661
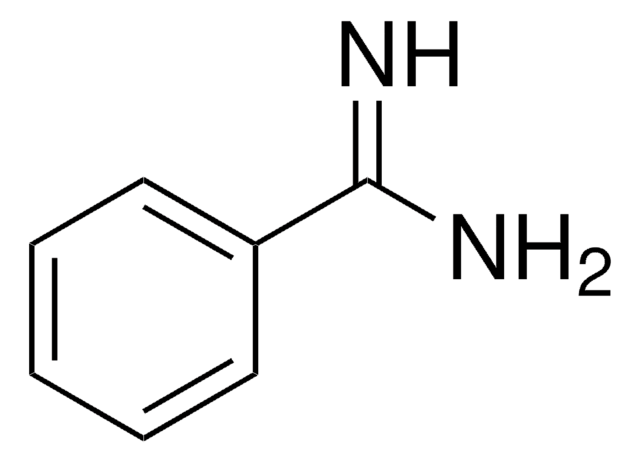
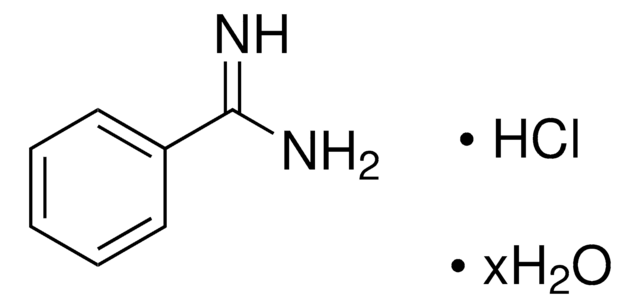
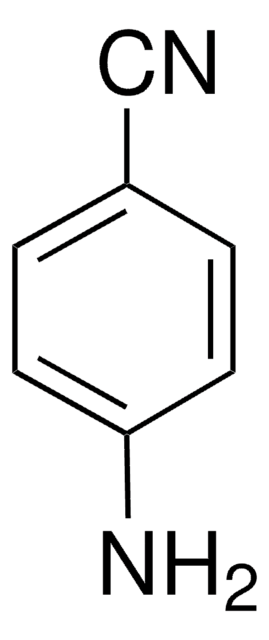
4-Aminobenzamidin -dihydrochlorid
98%
Synonym(e):
p-Aminobenzimidamide dihydrochloride
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(2)
About This Item
Lineare Formel:
H2NC6H4C(=NH)NH2·2HCl
CAS-Nummer:
Molekulargewicht:
208.09
Beilstein:
3692927
EG-Nummer:
MDL-Nummer:
UNSPSC-Code:
12352100
PubChem Substanz-ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Form:
crystals
Assay:
98%
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
98%
Form
crystals
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
>300 °C (lit.)
Funktionelle Gruppe
amine
Lagertemp.
2-8°C
SMILES String
Cl[H].Cl[H].NC(=N)c1ccc(N)cc1
InChI
1S/C7H9N3.2ClH/c8-6-3-1-5(2-4-6)7(9)10;;/h1-4H,8H2,(H3,9,10);2*1H
InChIKey
GHEHNICLPWTXJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Anwendung
Used as a ligand in affinity chromatography for purification and immobilization of enzymes.
4-Aminobenzamidine dihydrochloride can be used to synthesize:
- Orally active fibrinogen receptor antagonists based on benzamidines.
- Benzamidine derivatives that are selective and potent serine protease inhibitors.
- Novel pyrrolo [3,2-c] quinolines that are structural analogs of topoisomerase inhibitors such as coralyne and fagaronine.
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Biochemical and molecular modeling analysis of the ability of two p-aminobenzamidine-based sorbents to selectively purify serine proteases (fibrinogenases) from snake venoms.
De-Simone S G, et al.
Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 822(1-2), 1-9 (2005)
In vitro blood compatibility of polymeric biomaterials through covalent immobilization of an amidine derivative.
Gouzy M F, et al.
Biomaterials, 25(17), 3493-3501 (2004)
A L Nguyen et al.
Biotechnology and bioengineering, 34(9), 1186-1190 (1989-11-01)
Reactive polymers have been prepared by copolymeriz-ing N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAM) with N-acryloxy-succinimide (NASI) or glycidyl methacrylate (GMA). The amino groups of ligands could react with the residues of NASI or GMA and the polymers could be precipitated by temperature and/or
A L Nguyen et al.
Enzyme and microbial technology, 12(9), 663-668 (1990-09-01)
A reactive water-soluble polymer was synthesized by copolymerizing N-isopropylacrylamide and glycidyl acrylate. The reactive polymer could react with the amino groups of enzymes/proteins or other ligands to form an affinity polymer. As a model, the reactive polymer was allowed to
Specific adsorption of serine proteases on coated silica beads substituted with amidine derivatives.
S Khamlichi et al.
Journal of chromatography, 510, 123-132 (1990-06-27)
Amidine derivatives interact with serine proteases, the inhibition being due to interactions between amidine functions and the active sites of the enzymes. Five different types of amidine (substituted or unsubstituted) were coupled to coated silica beads, which had previously been
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.