661619
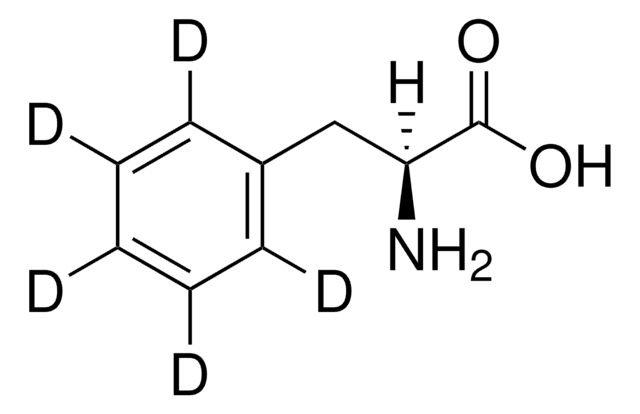
L-Phenyl-d5-Alanin
endotoxin tested, 98 atom % D
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Isotopenreinheit
98 atom % D
Form
solid
Optische Aktivität
[α]25/D -33.0°, c = 1 in H2O
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
270-275 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Eignung
endotoxin tested
Massenverschiebung
M+5
SMILES String
[H]C(N)(Cc1c([2H])c([2H])c([2H])c([2H])c1[2H])C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C9H11NO2/c10-8(9(11)12)6-7-4-2-1-3-5-7/h1-5,8H,6,10H2,(H,11,12)/t8-/m0/s1/i1D,2D,3D,4D,5D
InChIKey
COLNVLDHVKWLRT-HRVDQBBZSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Verwandte Kategorien
Anwendung
Endotoxin testing is done on the bulk form of the product before subdivision packaging. This bulk test does not guarantee that the subdivision or repackaged aliquot is endotoxin-free when it is received or used by the customer and does not imply suitability for any particular purpose. If the product must be endotoxin-free for the intended application, the product should be tested prior to actual use.
Verpackung
Analysenzertifikate (COA)
Suchen Sie nach Analysenzertifikate (COA), indem Sie die Lot-/Chargennummer des Produkts eingeben. Lot- und Chargennummern sind auf dem Produktetikett hinter den Wörtern ‘Lot’ oder ‘Batch’ (Lot oder Charge) zu finden.
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.