442631
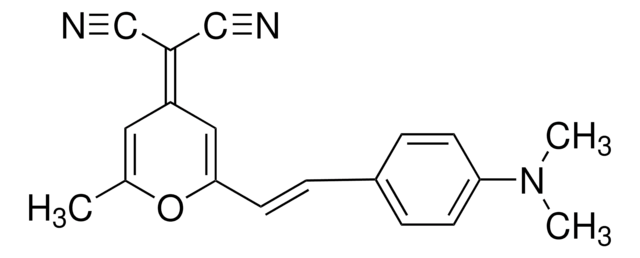
3-(2-Benzothiazolyl)-7-(diethylamino)-cumarin
98%
Synonym(e):
3-(2-Benzothiazolyl)-N,N-diethylumbelliferylamin, Cumarin 6
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
98%
Form
solid
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
208-210 °C (lit.)
λmax
444 nm
Fluoreszenz
λem 505 nm in ethanol (Lasing peak 534 nm, lasing range 515 - 558 nm (DMSO), pump source XeCl (308 nm))
Leistung von OLED-Bauelementen
ITO/Alq3:Coumarin 6/Mg:Ag
SMILES String
CCN(CC)c1ccc2C=C(C(=O)Oc2c1)c3nc4ccccc4s3
InChI
1S/C20H18N2O2S/c1-3-22(4-2)14-10-9-13-11-15(20(23)24-17(13)12-14)19-21-16-7-5-6-8-18(16)25-19/h5-12H,3-4H2,1-2H3
InChIKey
VBVAVBCYMYWNOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Anwendung
- in block copolymer (BCP)-based micelle based drug delivery studies in glioma cell lines
- in combination with flufenamic acid (FA) based nanoprodrug uptake in glioma cells
- in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) based elvitegravir nanoprodrug uptake studies
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
One of the common difficulties with intravenous drug delivery is low solubility of the drug. The requirement for large quantities of saline to dissolve such materials limits their clinical use, and one solution for this problem that has recently generated interest is the formation of drug-loaded micelles.
Developed in the last several years, fluorescence quenching microscopy (FQM) has enabled rapid, inexpensive, and high-fidelity visualization of two-dimensional (2D) materials such as graphene-based sheets and MoS2.
Graphene has emerged as the new wonder material. Being only one atom thick and composed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice structure, the interest in this material has exploded exponentially since 2004 when it was first isolated and identified using a very simple method.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.