Wichtige Dokumente
440744
Polycaprolacton
average Mn 80,000
Synonym(e):
2-Oxepanon Homopolymer, 6-Caprolacton Polymer
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Form
pellets (~3 mm)
Mol-Gew.
average Mn 80,000
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Eigenschaften
Design for Energy Efficiency
Use of Renewable Feedstocks
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Verunreinigungen
<0.5% water
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
60 °C (lit.)
Dichte
1.145 g/mL at 25 °C
Mw/Mn
<2
Anwendung(en)
3D bioprinting
advanced drug delivery
Grünere Alternativprodukt-Kategorie
SMILES String
C1CCC(=O)OCC1 (Canonical-SMILES)
InChI
1S/C6H10O2/c7-6-4-2-1-3-5-8-6/h1-5H2
InChIKey
PAPBSGBWRJIAAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
- Es zersetzt sich langsamer als andere biologisch abbaubare Polyester unter physiologischen Bedingungen. Diese Eigenschaft kann bei der allmählichen kontrollierten Freisetzung von Wirkstoffen in Zielgeweben genutzt werden.
- Seine schwach ausgeprägte Oberflächenbenetzung und Wechselwirkung mit biologischen Flüssigkeiten wegen seiner Hydrophobie bewirken eine schlechte Zelladhäsion und -proliferation, weshalb es mit anderen synthetischen/natürlichen Polymeren gemischt wird.
Anwendung
- Mit Antibiotika beladenes PCL kann zur Behandlung von Infektionen der Atemwege (z. B. Tuberkulose) verwendet werden.
- Es wurden Untersuchungen auf der Grundlage der phänotypischen Reaktion von humanen mesenchymalen Knochenmarkstammzellen (hBMSCs) für verschiedene Verhältnisse von Chitosan/Polycaprolacton (PCL)-Mischungen durchgeführt.
- PCL/biomedizinische Keramikmaterialien wurden auf eine potenzielle Regeneration von Knochengewebe hin untersucht.
- Wirkung von PCL/abgestuftem Insulin/beta-5-Glycerophosphat-Konzentrationen auf die Bildung von osteochondralem Gewebe durch die Differenzierung von aus Fettgewebe gewonnenen Stromazellen.
- Andere allgemeine Verwendungszwecke: Extrusionsmittel, Gesenkschmierstoffe, Gussformfreigabe, Pigment- und Füllstoffdispersionsmittel sowie Polyestersegmente in Urethanen und Blockpolyestern.
Leistungsmerkmale und Vorteile
Nicht toxisch, im Boden biologisch abbaubar, breite Mischbarkeit, mechanische Kompatibilität mit vielen Polymeren und gute Adhäsion an einem breiten Spektrum von Substraten.
Ähnliches Produkt
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
We will explore the technological advances that have contributed toward the progress of 3DP of tissue engineering scaffolds, current materials used to create 3DP scaffolds, and the challenges that remain.
In the past two decades, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have become important interdisciplinary fields that span biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine.
Innovations in polymer technology have had a significant impact on the advancement of novel drug delivery systems.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.

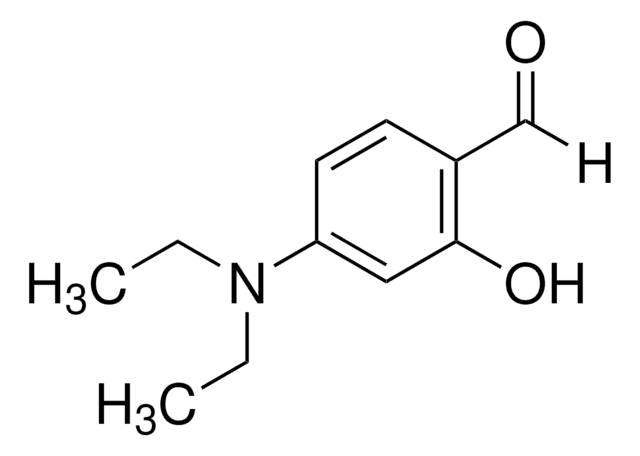
![2,3,6,7-Tetrahydro-8-hydroxy-1H,5H-benzo[ij]chinolizin-9-carboxaldehyd 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/166/830/a0d9a84a-5623-41a1-a54b-3b0272e5b28c/640/a0d9a84a-5623-41a1-a54b-3b0272e5b28c.png)