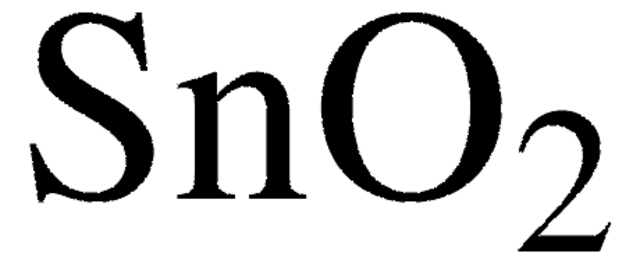Alle Fotos(4)
Wichtige Dokumente
244651
Zinn(IV)-Oxid
−325 mesh, 99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(e):
Zinnoxid
Anmeldenzur Ansicht organisationsspezifischer und vertraglich vereinbarter Preise
Alle Fotos(4)
About This Item
Lineare Formel:
SnO2
CAS-Nummer:
Molekulargewicht:
150.71
EG-Nummer:
MDL-Nummer:
UNSPSC-Code:
12352303
PubChem Substanz-ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Empfohlene Produkte
Qualitätsniveau
Assay
99.9% trace metals basis
Form
powder
Partikelgröße
−325 mesh
Dichte
6.95 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Anwendung(en)
battery manufacturing
SMILES String
O=[Sn]=O
InChI
1S/2O.Sn
InChIKey
XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Suchen Sie nach ähnlichen Produkten? Aufrufen Leitfaden zum Produktvergleich
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Tin(IV) oxide (SnO2) is an n-type wide band gap semiconductor with high transmittance at nearIR and visible region. It is scratch resistant and chemically inert.
Anwendung
Tin(IV) oxide has been used to prepare thin films of TiO2-doped SnO2 oxide nanocomposites.
It can be used as astarting material to prepare niobium and zinc-doped titanium-tin-oxidesolid-solution ceramics, which are applicable in the field of electronicdevices.
It can be used as astarting material to prepare niobium and zinc-doped titanium-tin-oxidesolid-solution ceramics, which are applicable in the field of electronicdevices.
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
nwg
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Gun-Joo Sun et al.
Nanotechnology, 24(2), 025504-025504 (2012-12-15)
Networked SnO(2) nanowire sensors were achieved using the selective growth of SnO(2) nanowires and their tangling ability, particularly on on-chip V-groove structures, in an effort to overcome the disadvantages imposed on the conventional trench-structured SnO(2) nanowire sensors. The sensing performance
Li-Ping Li et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 49(17), 1762-1764 (2013-01-25)
ZnSn(OH)(6) and binary-component SnO(2)-ZnSn(OH)(6) were introduced as affinity probes for phosphopeptide enrichment for the first time. Two strategies, either ZnSn(OH)(6) and SnO(2) serial enrichment or binary-component SnO(2)-ZnSn(OH)(6) enrichment in a single run, were proposed to enhance multi-phosphopeptide enrichment and to
Dawei Su et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 49(30), 3131-3133 (2013-03-13)
An in situ hydrothermal synthesis approach has been developed to prepare SnO2@graphene nanocomposites. The nanocomposites exhibited a high reversible sodium storage capacity of above 700 mA h g(-1) and excellent cyclability for Na-ion batteries. In particular, they also demonstrated a
Linlin Li et al.
Nanoscale, 5(1), 134-138 (2012-11-14)
Novel eggroll-like CaSnO(3) nanotubes have been prepared by a single spinneret electrospinning method followed by calcination in air for the first time. The electrospun sample as a lithium-ion battery electrode material exhibited improved cycling stability and rate capability by virtue
Yinzhu Jiang et al.
ACS applied materials & interfaces, 4(11), 6216-6220 (2012-10-31)
Porous SnO₂/graphene composite thin films are prepared as anodes for lithium ion batteries by the electrostatic spray deposition technique. Reticular-structured SnO₂ is formed on both the nickel foam substrate and the surface of graphene sheets according to the scanning electron
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.