C0400
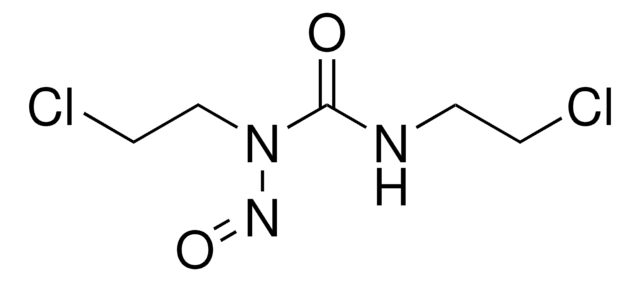
Carmustine
≥98% (TLC), oily liquid to amorphous solid, DNA alkylating agent
Sinónimos:
1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea, BCNU
About This Item
Productos recomendados
product name
Carmustine, ≥98%
Quality Level
assay
≥98%
form
(Oily liquid to amorphous solid)
mp
30 °C (lit.)
solubility
ethanol: 19.60-20.40 mg/mL, clear, pale yellow to yellow
originator
Bristol-Myers Squibb
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
ClCCNC(=O)N(CCCl)N=O
InChI
1S/C5H9Cl2N3O2/c6-1-3-8-5(11)10(9-12)4-2-7/h1-4H2,(H,8,11)
InChI key
DLGOEMSEDOSKAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... GSR(2936)
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Oral - Carc. 1B - Repr. 1B
Storage Class
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
DNA damage and repair mechanism is vital for maintaining DNA integrity. Damage to cellular DNA is involved in mutagenesis, the development of cancer among others.
Contenido relacionado
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is a selective process for the removal of unnecessary, infected or transformed cells in various biological systems. As it plays a role in the homeostasis of multicellular organisms, apoptosis is tightly regulated through two principal pathways by a number of regulatory and effector molecules.
n proliferating cells, the cell cycle consists of four phases. Gap 1 (G1) is the interval between mitosis and DNA replication that is characterized by cell growth. Replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis (S) phase, which is followed by a second gap phase (G2) during which growth and preparation for cell division occurs. Together, these three stages comprise the interphase phase of the cell cycle. Interphase is followed by the mitotic (M) phase.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico