T7039
Transforming Growth Factor-β1 human
≥98% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
hTGF-β1, TGF-β1
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Transforming Growth Factor-β1 human, TGF-β1, recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, powder, suitable for cell culture
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in CHO cells
Assay
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
form
powder
potency
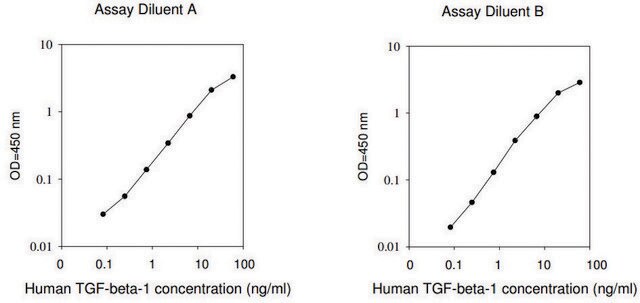
≤0.05 ng/mL ED50
quality
endotoxin tested
mol wt
protein 25 kDa
packaging
pkg of 2 μg
pkg of 50 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
<1 EU/μg
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... TGFB1(7040)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
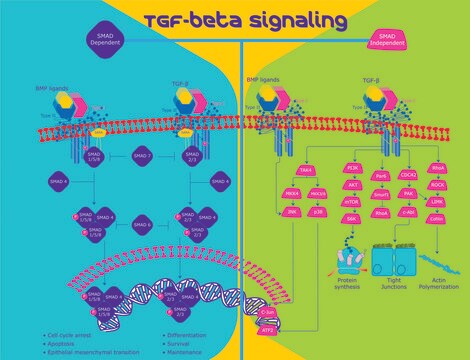
General description
Application
- reporter gene assay.
- in vitro transfection.
- to study the effect of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) on gene array analysis of renal cells.
- to study the association of TGF-β1 with shear stress-dependent upregulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in microvascular endothelial cells.
- to study the interaction between TGF-β1 activation and myofibroblast formation.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Analysis Note
comparable product
recommended
related product
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Naive pluripotent stem cells are located within the epiblast of mature blastocysts. These primitive “ground-state” cells may be cultured in vitro using specialized media and small molecule inhibitors.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service