L6529
Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli O55:B5
γ-irradiated, BioXtra, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
LPS
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Escherichia coli (O55:B5)
Quality Level
sterility
γ-irradiated
product line
BioXtra
form
lyophilized powder
purified by
gel-filtration chromatography
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
<3% Protein (Lowry)
solubility
H2O: 5 mg/mL, faintly hazy to hazy
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
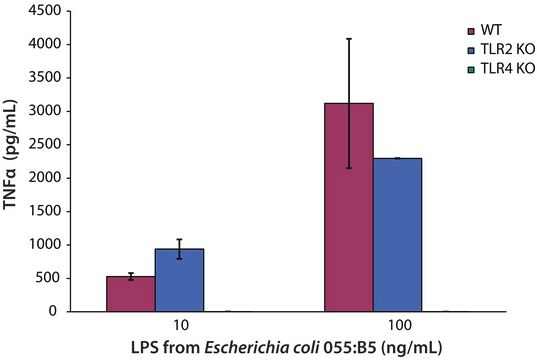
- to stimulate human PBMC to secrete cytokine.
- to stimulate wild type embryonic fibroblasts and mutants for the induction of phosphorylation of p56
- in the measurement of tumor necrosis factor-α levels and nuclear factor-κB p65 activities after stimulation
- in the stimulation of hamster lymphocytes in vitro
- to induce activated dendritic morphology in murine macrophage cell line in a study
Biochem/physiol Actions
Reconstitution
Other Notes
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 2 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
An overview of human microbiome research, workflow challenges, sequencing, library production, data analysis, and available microbiome reagents to support your research.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service