B8756
Bile salts
suitable for microbiology
Synonym(s):
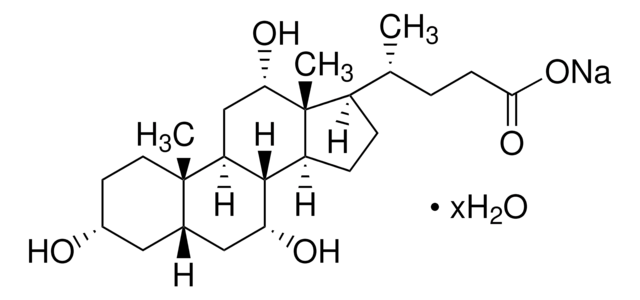
Bile acids sodium salt, cholic acid-deoxycholic acid sodium salt mixture
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106212
NACRES:
NA.85
Recommended Products
sterility
non-sterile
Quality Level
form
powder
solubility
distilled water: freely soluble
application(s)
microbiology
storage temp.
10-30°C
General description
Bile salt is an organic sodium salt with a conjugate of any of the bile acids along with either glycine or taurine. Biles salts are composed of four different kinds of bile acids - cholic, deoxycholic, chenodeoxycholic and lithocholic acids.Bile salts are extracted under controlled conditions from purified fresh bile, to be used in bacteriological culture media, where it behaves as a selective inhibitory agent that enables isolation and identification of pathogens. For example, in MacConkey Agar/Broth.
Application
Bile salts may be used as one of the selective agents to prevent the growth of injured Escherichia coli cells, in an experiment done in order to identify the specific agent in the selective media which would inhibit the growth of the injured Escherichia coli ML30 cells. It may also be used for identification of isolates of Vibrio (Beneckea) vulnificus which is a halophilic bacterium, found responsible for causing several human infections.
Other Notes
Mixture of sodium cholate and sodium deoxycholate
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Daniela Andrea Ramirez et al.
Food chemistry, 215, 493-500 (2016-08-21)
Organosulphur compounds (OSCs) present in garlic (Allium sativum L.) are responsible of several biological properties. Functional foods researches indicate the importance of quantifying these compounds in food matrices and biological fluids. For this purpose, this paper introduces a novel methodology
Christina S Faherty et al.
Molecular microbiology, 85(1), 107-121 (2012-05-11)
Shigella flexneri is a Gram-negative pathogen that invades the colonic epithelium. While invasion has been thoroughly investigated, it is unknown how Shigella first attaches to the epithelium. Previous literature suggests that Shigella utilizes adhesins that are induced by environmental signals
Lian-Hua Cui et al.
Journal of microbiology and biotechnology, 28(4), 510-519 (2018-02-01)
Synbiotics are a combination of probiotics and prebiotics, which lead to synergistic benefits in host welfare. Probiotics have been used as an alternative to antibiotics. Among the probiotics, Pediococcus acidilactici (PA) has shown excellent antimicrobial activity against Salmonella Gallinarum (SG)
Gordana Panic et al.
Parasites & vectors, 6, 237-237 (2013-08-15)
Echinostomiasis is one of the major food-borne trematodiases and the species Echinostoma caproni serves as a useful model for trematocidal drug discovery. The current in vitro drug sensitivity assay uses adult E. caproni worms that are incubated with candidate drugs
Luis Noriega et al.
International journal of food microbiology, 94(1), 79-86 (2004-06-03)
Six derivatives with increased resistance to ox gall (MIC: > or = 1% w/v) and one derivative resistant to sodium cholate (MIC: 0.8% w/v) were obtained from more sensitive original Bifidobacterium strains. These microorganisms, and two additional cholate resistant derivatives
Articles
The liver excretes excess cholesterol in the form of bile acids. Bile acids serve two purposes: to remove unwanted cholesterol from the body and to aid in lipid digestion in the intestine.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service