03450
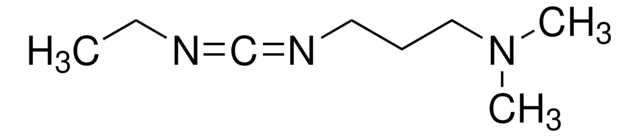
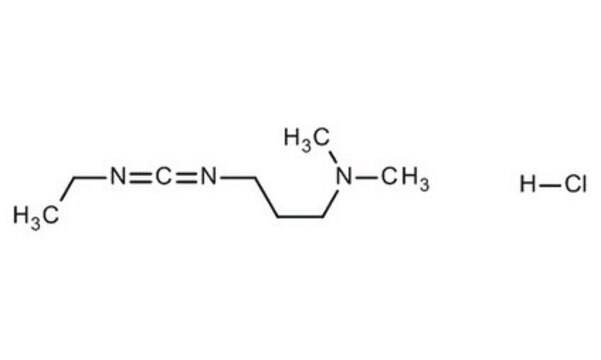
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
purum, ≥98.0% (AT)
Synonym(s):
N-Ethyl-N′-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDAC, EDC, EDC hydrochloride, WSC hydrochloride
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
purum
Quality Level
Assay
≥98.0% (AT)
form
powder
mp
110-115 °C (lit.)
110-115 °C
solubility
H2O: soluble 1 gm/10 ml, clear to very slightly hazy, colorless to very faintly yellow
application(s)
microbiology
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H17N3.ClH/c1-4-9-8-10-6-5-7-11(2)3;/h4-7H2,1-3H3;1H
InChI key
FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
The adaptability of EDAC HCl encompasses nucleic acid modification, permitting the selective labeling of DNA and RNA through their 5′ phosphate groups. This capacity contributes significantly to the visualization, tracking, and analytical aspects of these fundamental molecules, thereby advancing nucleic acid research. Furthermore, EDAC HCl functions as a biomolecule bridge, acting as a crosslinker connecting amine-reactive NHS-esters of biomolecules to carboxyl groups.
This feature proves invaluable in protein conjugation, facilitating the development of hybrid molecules with distinct properties and functions. The underlying reaction mechanism involves EDAC HCl′s interaction with a carboxyl group, forming an unstable intermediate actively seeking an amine partner. The delicate equilibrium of this reaction underscores the necessity for optimizing conditions to ensure efficient conjugation. The assistance of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) enhances the capabilities of EDAC HCl by stabilizing the intermediate and enabling two-step conjugation procedures, affording greater flexibility and control, particularly in the manipulation of complex biomolecular structures.
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Other Notes
comparable product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Target Organs
Stomach,large intestine,lymph node
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Carbodiimide-mediated peptide coupling remains to the most frequently used technique.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service