FAK100
Actin Cytoskeleton / Focal Adhesion Staining Kit
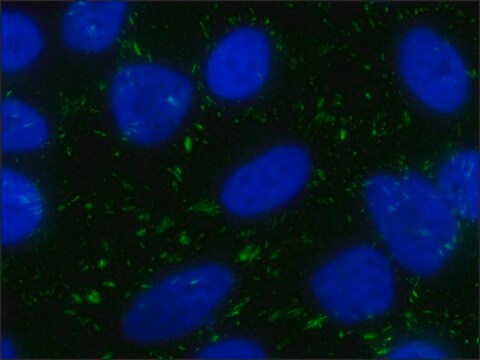
The Actin Cytoskeleton & Focal Adhesion Staining Kit consists of TRITC-conjugated phalloidin, anti-Vinculin & DAPI for the immunofluorescent staining of actin filaments in the cytoskeleton as well as the nucleus of the cells.
Synonym(s):
Actin Staining Kit
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352207
eCl@ss:
32161000
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
species reactivity
bovine, pig, human, rabbit
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
shipped in
wet ice
General description
The Actin Cytoskeleton and Focal Adhesion Staining Kit consists of three components (TRITC-conjugated phalloidin, anti-Vinculin and DAPI) for the immunofluorescent staining of actin filaments in the cytoskeleton, focal contacts as well as the nucleus of the cells.
Reagents and materials supplied in the Actin Cytoskeleton and Focal Adhesion Staining Kit are sufficient for 100 tests (including controls).
Introduction
The actin cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic network composed of actin polymers and a large variety of associated proteins. The functions of the actin cytoskeleton is to mediate a variety of essential biological functions in all eukaryotic cells, including intra- and extra-cellular movement and structural support. To perform these functions, the organization of the actin cytoskeleton must be tightly regulated both temporally and spatially. Many proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton are thus likely targets of signaling pathways controlling actin assembly. Actin cytoskeleton assembly is regulated at multiple levels, including the organization of actin monomers (G-protein) into actin polymers and the superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network (F-actin - the major constituent of microfilaments) [1]. This superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network is mediated by actin side-binding or cross-linking proteins [2, 3, 4]. Actin cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure that rapidly changes shape and organization in reponse to stimuli and cell cycle progression. Therefore, a disruption of its normal regulation may lead to cell transformations, hence cancer. Transformed cells have been shown to contain less F-actin than untransformed cells and exhibit atypical coordination of F-actin levels to the cell cycle [5]. Orientational distribution of actin filaments within a cell is an important determinant of cellular shape and motility. Therefore,
Focal adhesion and adherens junctions are membrane-associated complexes that serve as nucleation sites for actin filaments and as cross-linkers between the cell exterior, plasma membrane and actin cytoskeleton [6]. The function of focal adhesions are structural, linking the ECM on the outside to the actin cytoskeleton on the inside. They are also sites of signal transduction, initiating of signaling pathways in response to adhesion. Focal adhesions consist of integrin-type receptors that are attached to the extracellular matrix and are intracellularly associated with protein complexes containing vinculin (universal focal adhesion marker), talin, a-actinin, paxillin, tensin, zyxin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) [7,8].
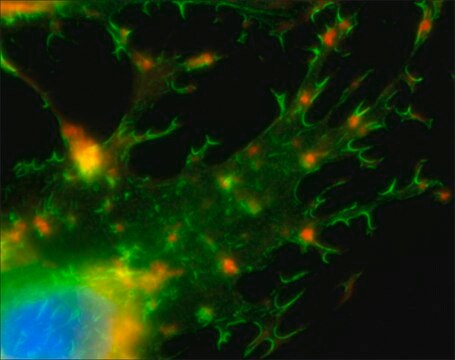
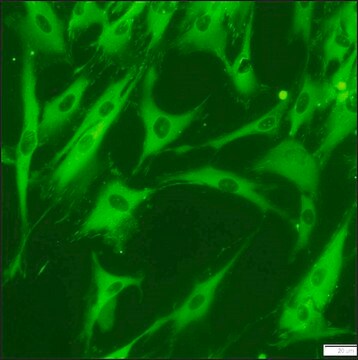
CHEMICON′s Actin Cytoskeleton and Focal Adhesion Staining Kit (Catalog number FAK100) is a very sensitive immunocytochemical tool that contains fluorescent-labeled phalloidin (TRITC-conjugated phalloidin) to map the local orientation of actin filaments within cell and a mouse monoclonal antibody to Vinculin that is very specific for the staining of focal contacts in cells.
Reagents and materials supplied in the Actin Cytoskeleton and Focal Adhesion Staining Kit are sufficient for 100 tests (including controls).
Introduction
The actin cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic network composed of actin polymers and a large variety of associated proteins. The functions of the actin cytoskeleton is to mediate a variety of essential biological functions in all eukaryotic cells, including intra- and extra-cellular movement and structural support. To perform these functions, the organization of the actin cytoskeleton must be tightly regulated both temporally and spatially. Many proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton are thus likely targets of signaling pathways controlling actin assembly. Actin cytoskeleton assembly is regulated at multiple levels, including the organization of actin monomers (G-protein) into actin polymers and the superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network (F-actin - the major constituent of microfilaments) [1]. This superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network is mediated by actin side-binding or cross-linking proteins [2, 3, 4]. Actin cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure that rapidly changes shape and organization in reponse to stimuli and cell cycle progression. Therefore, a disruption of its normal regulation may lead to cell transformations, hence cancer. Transformed cells have been shown to contain less F-actin than untransformed cells and exhibit atypical coordination of F-actin levels to the cell cycle [5]. Orientational distribution of actin filaments within a cell is an important determinant of cellular shape and motility. Therefore,
Focal adhesion and adherens junctions are membrane-associated complexes that serve as nucleation sites for actin filaments and as cross-linkers between the cell exterior, plasma membrane and actin cytoskeleton [6]. The function of focal adhesions are structural, linking the ECM on the outside to the actin cytoskeleton on the inside. They are also sites of signal transduction, initiating of signaling pathways in response to adhesion. Focal adhesions consist of integrin-type receptors that are attached to the extracellular matrix and are intracellularly associated with protein complexes containing vinculin (universal focal adhesion marker), talin, a-actinin, paxillin, tensin, zyxin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) [7,8].
CHEMICON′s Actin Cytoskeleton and Focal Adhesion Staining Kit (Catalog number FAK100) is a very sensitive immunocytochemical tool that contains fluorescent-labeled phalloidin (TRITC-conjugated phalloidin) to map the local orientation of actin filaments within cell and a mouse monoclonal antibody to Vinculin that is very specific for the staining of focal contacts in cells.
Application
Research Category
Cell Structure
Cell Structure
Research Sub Category
Cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
Components
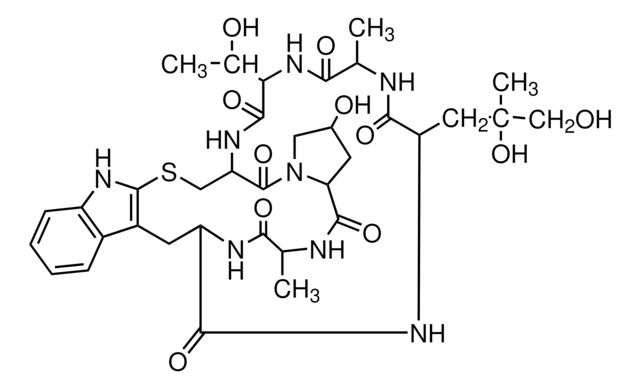
Vinculin Monoclonal antibody, purified clone 7F9 (Part No. 90227). One vial containing 100 μL at 1 mg/mL.
TRITC-conjugated Phalloidin (Part No. 90228). One vial containing 15 μg.
DAPI (Part No. 90229). One vial containing 100 μL.
TRITC-conjugated Phalloidin (Part No. 90228). One vial containing 15 μg.
DAPI (Part No. 90229). One vial containing 100 μL.
Storage and Stability
When stored at 2-8º C, the kit components are stable up to the expiration date. Do not freeze or expose to elevated temperatures. Discard any remaining reagents after the expiration date.
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Flam. Liq. 2 - STOT SE 1
Target Organs
Eyes,Central nervous system
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
High intracellular iron oxide nanoparticle concentrations affect cellular cytoskeleton and focal adhesion kinase-mediated signaling.
Soenen SJ, Nuytten N, De Meyer SF, De Smedt SC, De Cuyper M
Small null
Patterning discrete stem cell culture environments via localized self-assembled monolayer replacement.
JT Koepsel, WL Murphy
Langmuir null
A novel gellan gel-based microcarrier for anchorage-dependent cell delivery.
Chunming Wang, Yihong Gong, Yongming Lin, Jiangbo Shen, Dong-An Wang
Acta Biomaterialia null
RGD peptide-conjugated poly(dimethylsiloxane) promotes adhesion, proliferation, and collagen secretion of human fibroblasts
Li, Bin, et al
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 79, 989-998 (2006)
Wilms' tumor gene WT1 17AA(-)/KTS(-) isoform induces morphological changes and promotes cell migration and invasion in vitro.
Jomgeow, Tanyarat, et al.
Cancer Science, 97, 259-270 (2006)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service