AABG02500
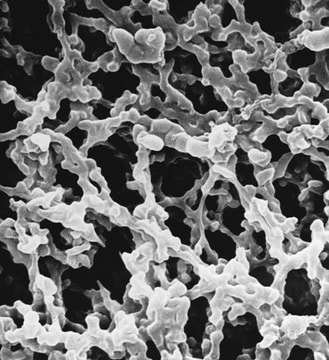
MCE Membrane Filter, 0.8 μm Pore Size
MF-Millipore™, filter diam. 25 mm, hydrophilic, black, gridded
Synonym(s):
Gridded mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane filter discs, MF-Millipore™ Membrane Filter, 0.8 µm pore size, gridded
About This Item
Recommended Products
material
black filter
gridded
mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane
Quality Level
description
25 mm diameter, mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, hydrophilic, black, gridded, 100 discs
sterility
non-sterile
feature
hydrophilic
manufacturer/tradename
MF-Millipore™
Millipore
parameter
16 L/min-cm2 air flow rate
190 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate
75 °C max. temp.
filter diam.
25 mm
thickness
150 μm
gravimetric extractables
4%
color
black
matrix
MF-Millipore™
pore size
0.8 μm pore size
82 % porosity
bubble point
≥1.0 bar, air with water at 23 °C
shipped in
ambient
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- Fluorescent assays
- Particle monitoring
- Air monitoring
- Microplastics
Features and Benefits
- Applicable for biological and environmental samples.
- Available in variable pore sizes, black or white color.
- Autoclavable and compatible with ethylene oxide and gamma irradiation
Legal Information
also commonly purchased with this product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Sol. 1
Storage Class Code
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service