930717
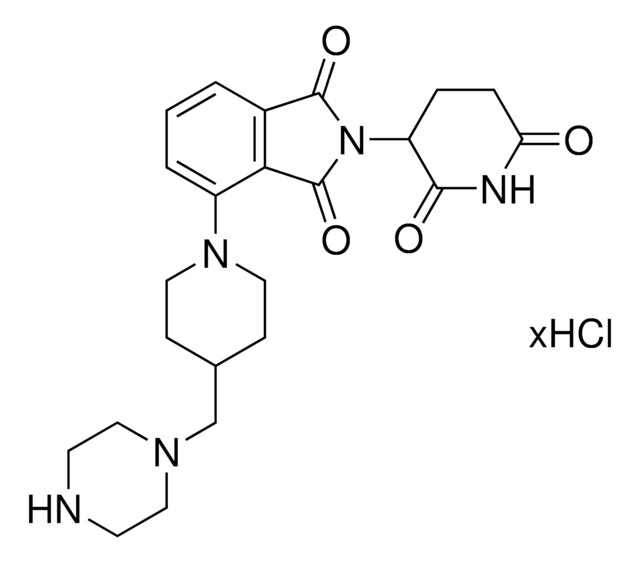
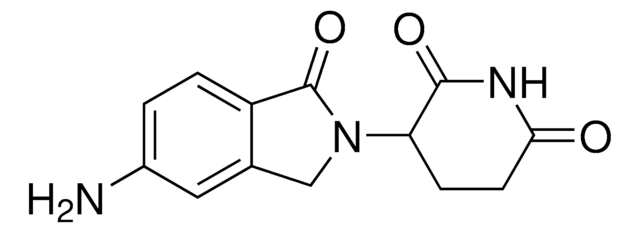
1H-Isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, 2-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)-5-(4-piperidinyloxy) hydrochloride
≥95%
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C18H19N3O5 · xHCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
357.36 (free base basis)
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352101
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95%
form
powder
functional group
amine
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O=C1NC(C(CC1)N2C(C3=CC=C(C=C3C2=O)OC4CCNCC4)=O)=O
Application
1H-Isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione, 2-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)-5-(4-piperidinyloxy) Hydrochloride is a functionalized Cereblon ligand used for development of protein degrader building blocks. Contains a terminal amine group, allowing rapid conjugation of carboxyl containing linkers. A basic building block for development of a protein degrader library.
Technology Spotlight: Degrader Building Blocks for Targeted Protein Degradation
Protein Degrader Building Blocks
Technology Spotlight: Degrader Building Blocks for Targeted Protein Degradation
Protein Degrader Building Blocks
Other Notes
Targeted Protein Degradation by Small Molecules
Destruction of DNA-Binding Proteins by Programmable Oligonucleotide PROTAC (O′PROTAC): Effective Targeting of LEF1 and ERG
Small-Molecule PROTACS: New Approaches to Protein Degradation
Targeted Protein Degradation: from Chemical Biology to Drug Discovery
Impact of linker length on the activity of PROTACs
Destruction of DNA-Binding Proteins by Programmable Oligonucleotide PROTAC (O′PROTAC): Effective Targeting of LEF1 and ERG
Small-Molecule PROTACS: New Approaches to Protein Degradation
Targeted Protein Degradation: from Chemical Biology to Drug Discovery
Impact of linker length on the activity of PROTACs
Legal Information
PROTAC® is a registered trademark of Arvinas Operations, Inc., and is used under license.
PROTAC is a registered trademark of Arvinas Operations, Inc., and is used under license
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Repr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Daniel P Bondeson et al.
Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 57, 107-123 (2016-10-13)
Protein homeostasis networks are highly regulated systems responsible for maintaining the health and productivity of cells. Whereas therapeutics have been developed to disrupt protein homeostasis, more recently identified techniques have been used to repurpose homeostatic networks to effect degradation of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service