777676
Graphene oxide dispersion
4 mg/mL,dispersion in H2O, avg. no. of layers, 1
Synonym(s):
GO dispersion in H2O
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Graphene oxide, 4 mg/mL, dispersion in H2O, avg. no. of layers, 1
description
dispersibility: Polar solvents
Quality Level
form
dispersion in H2O
feature
avg. no. of layers 1 measured in 0.5mg/mL (>95%)
avg. no. of layers 1
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
concentration
4 mg/mL
greener alternative category
, Enabling
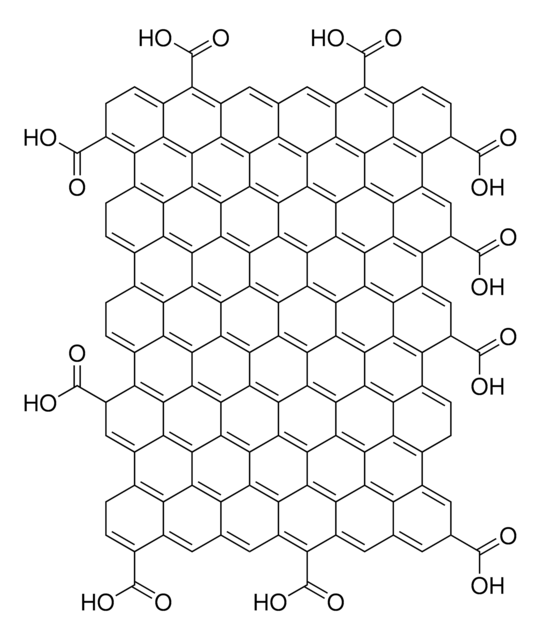
SMILES string
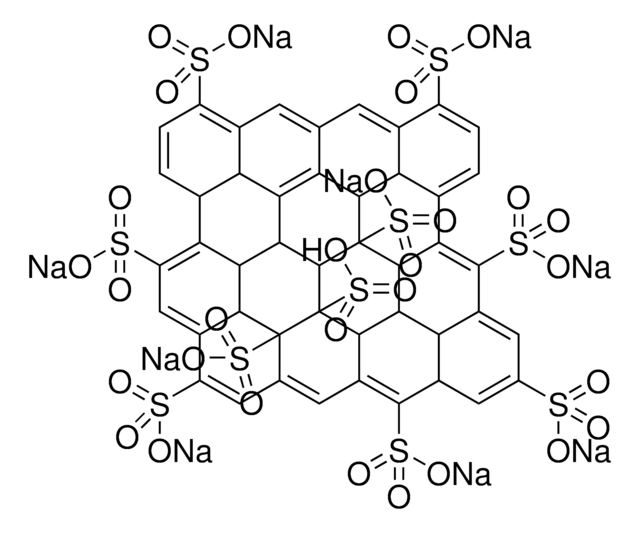
O=C(O)C1C2=C3C4=C5C6=C7C8=C9C%10=C%11C(C%12=C%13C%10=C%14C8=C%15C6=C%16C4=C%17C2=CC(C(O)=O)C%18=C%17C%19=C%16C%20=C%15C%21=C%14C%22=C%13C(C%23=C%24C%22=C%25C%21=C%26C%20=C%27C%19=C%28C%18=CC(C(O)=O)C%29=C%28C%30=C%27C%31=C%26C%32=C%25C%33=C%24C(C%34=C%35C
InChI
1S/C140H42O20/c141-131(142)26-13-23-15-44-62(140(159)160)45-16-24-14-40-31(132(143)144)5-1-29-41-20-48(135(149)150)56-33-7-3-28-27-2-6-32-55-37(133(145)146)11-9-35-60(138(155)156)42-17-25-18-43-61(139(157)158)36-10-12-38(134(147)148)58-46-21-50(137(153)154)59-47-22-49(136(151)152)57-34-8-4-30-39(19-26)51(23)78-72(44)88-75(45)80-52(24)79(54(29)40)95-71(41)83(56)101-93-69(33)64(28)91-90-63(27)68(32)92-86(66(35)55)73(42)81-53(25)82-74(43)87(67(36)58)96-76(46)85(59)103-97-77(47)84(57)102-94-70(34)65(30)89(78)105-104(88)115-98(80)111(95)116(101)126-122-110(93)107(91)120-119-106(90)108(92)99(81)114-100(82)112(96)118(103)128(124(114)119)123-113(97)117(102)127(130(122)129(120)123)121(109(94)105)125(115)126/h2,5,7-10,12-22,26,38,48-50H,1,3-4,6,11H2,(H,141,142)(H,143,144)(H,145,146)(H,147,148)(H,149,150)(H,151,152)(H,153,154)(H,155,156)(H,157,158)(H,159,160)
InChI key
VTWITIAIMADGRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Storage and Stability
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
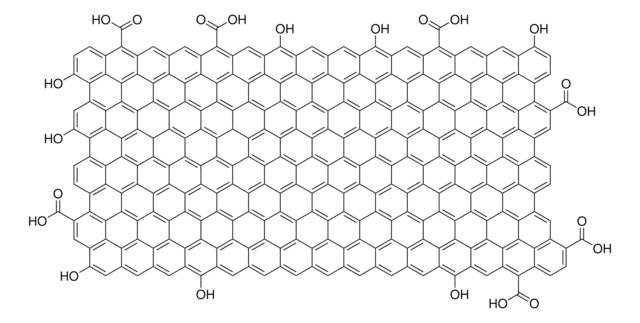
Graphene oxide is a unique material that can be viewed as a single monomolecular layer of graphite with various oxygen containing functionalities such as epoxide, carbonyl, carboxyl and hydroxyl groups.
Carbon nanomaterials (CNMs), such as single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), and graphene (Figure 1), have diverse commercial applications including lighter and stronger composite materials, improved energy storage devices, more sensitive sensors, and smaller transistors.
Professor Ebrahimi and Professor Robinson (Pennsylvania State University, USA) summarize recent advances in the synthesis of these 2D materials, resulting material properties, and related applications in biosensing of neurotransmitters, metabolites, proteins, nucleic acids, bacterial cells, and heavy metals.
Recent demand for electric and hybrid vehicles, coupled with a reduction in prices, has caused lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) to become an increasingly popular form of rechargeable battery technology.
Related Content
Batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors rely on electrochemical energy production. Understand their operation and electron/ion transport separation.
Batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors rely on electrochemical energy production. Understand their operation and electron/ion transport separation.
Batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors rely on electrochemical energy production. Understand their operation and electron/ion transport separation.
Batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors rely on electrochemical energy production. Understand their operation and electron/ion transport separation.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service