76153
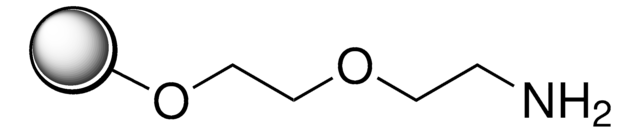
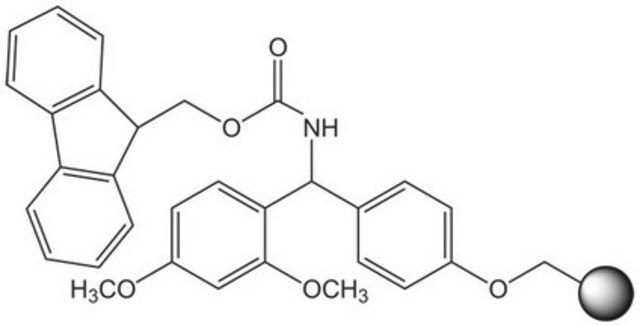
PEGA resin
extent of labeling: ~0.4 mmol/g loading
Synonym(s):
Poly[acryloyl-bis(aminopropyl)polyethylene glycol]
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
product line
PEGA
Quality Level
form
crystals
reaction suitability
reaction type: Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis
extent of labeling
~0.4 mmol/g loading
impurities
90% methanol
particle size
150-300 μm
functional group
amine
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
PEGA resins are a hydrophilic acrylamide-PEG co-polymer providing a really extensive and more uniform swelling in a wide range of solvents (from water, methanol, ethanol to tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and toluene). The extreme swelling volume of this support in the standard peptide synthesis solvents DCM and DMF together with their good stability make them ideally suited for the batch as well as for continuous-flow syntheses.
Application
Polyacrylamide resin possessing long polyethylene glycol spacers giving extremely high swell resin may be used for:
- immobilizing enzymes in aqueous solution
- affinity purification of small-molecule binding proteins
- synthesis of peptide libraries with fluorescently labeled proteins
Packaging
Sold on basis of weight of dry resin.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Identification of small molecule binding molecules by affinity purification using a specific ligand immobilized on PEGA resin.
Kuramochi K, et al.
Bioconjugate Chemistry, 19(12), 2417-2426 (2008)
A PEGA resin for use in the solid-phase chemical?enzymatic synthesis of glycopeptides.
Meldal M, et al.
Journal of the Chemical Society. Chemical Communications, 16, 1849-1850 (1994)
Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility of PEGA resins.
Auzanneau FI, et al.
Journal of Peptide Science, 1(1), 31-44 (1995)
Chemical ligation of unprotected peptides directly from a solid support.
Camarero JA, et al.
The Journal of Peptide Research, 51(4), 303-316 (1998)
Catch and release of concanavalin A by a mannose-immobilized photoaffinity PEGA resin coupled with a cleavable disulfide linker.
Kuramochi K, et al.
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 79(12), 1946-1953 (2015)
Related Content
The high swelling volume of PEGA resins makes the functionalities located within the polymer bead accessible to large biomolecules.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service