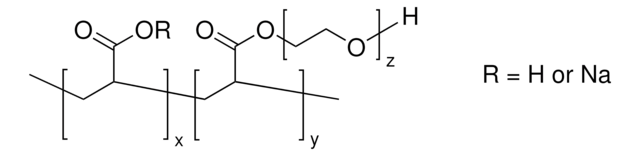
738743
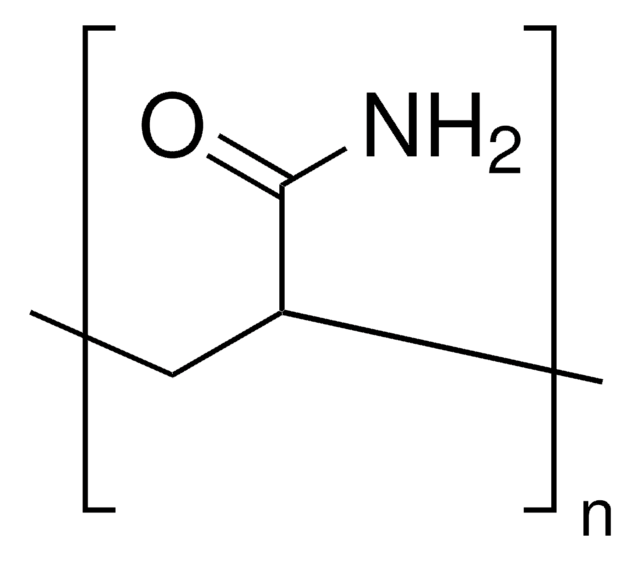
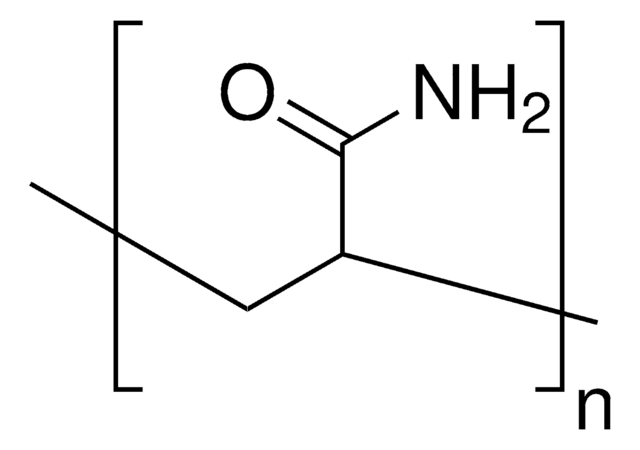
Polyacrylamide
average Mn 40,000
Synonym(s):
PAM
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
powder
Quality Level
mol wt
average Mn 40,000
mp
246-250 °C
transition temp
Tm 246-250 °C
InChI
1S/C3H5NO/c1-2-3(4)5/h2H,1H2,(H2,4,5)
InChI key
HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Proteomic analysis and lethality of the venom of Aegaeobuthus nigrocinctus, a scorpion of medical significance in the Middle East.: This study utilized polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) to analyze the protein composition of the venom, providing insights into its biochemical properties and potential medical applications. The results highlight the importance of PAGE in venom proteomics and its relevance in biomedical research (Borges et al., 2024).
- One-Dimensional Acrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for Analysis of Plant Samples.: This paper describes the methodology of using PAGE for the analysis of plant proteins, demonstrating its utility in biochemistry and molecular biology studies. The technique is essential for separating and identifying proteins in complex mixtures, underscoring its significance in research and development in the life sciences (Marzban et al., 2024).
- Protocol for isolating small cytosolic dsDNA from cultured murine cells.: The study outlines a detailed protocol incorporating PAGE for the isolation and analysis of small cytosolic dsDNA from murine cells. This method is pivotal for research in molecular and cellular biology, facilitating advancements in genetic and biomedical studies (Dai et al., 2024).
- Comparative study of the commonly used protein quantitation assays on different Hymenoptera venoms: A fundamental aspect of Hymenoptera venom proteome analysis.: This research compares various protein quantitation assays, including PAGE, to analyze Hymenoptera venoms. The findings underscore the critical role of PAGE in proteomic analysis and its application in toxinology and biomedical research (Wanandy et al., 2024).
- Proteomics and Its Current Application in Biomedical Area: Concise Review.: This review highlights the applications of proteomics, including PAGE, in biomedical research. It discusses the advancements and future directions in the field, emphasizing the importance of PAGE in proteomic studies and its contributions to biomedical science (Gobena et al., 2024).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
[Improvement of polyacrylamide gel media for electrophoresis: enhancement of elasticity by polymer blending].
K Aizawa
Tanpakushitsu kakusan koso. Protein, nucleic acid, enzyme, 43(15), 2191-2198 (1998-12-30)
D J King et al.
Reviews on environmental health, 8(1-4), 3-16 (1989-01-01)
The purpose of this paper is to present information gathered regarding, in general, the physical characteristics, and, in particular, the possible toxic nature of polyacrylamide A short discussion of the properties and toxicity of the acrylamide monomer is also included.
Sachio Yamamoto
Yakugaku zasshi : Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, 132(9), 1031-1035 (2012-10-02)
Microchip electrophoresis is widely used for microfluidics and has been studied extensively over the past decade. Translation of capillary electrophoresis methods from traditional capillary systems to a microchip platform provides rapid separation and easy quantitation of sample components. However, most
International journal of toxicology, 24 Suppl 2, 21-50 (2005-09-13)
Polyacrylamide is a polymer of controllable molecular weight formed by the polymerization of acrylamide monomers available in one of three forms: solid (powder or micro beads), aqueous solution, or inverse emulsions (in water droplets coated with surfactant and suspended in
Xiaohu Dai et al.
Scientific reports, 5, 11675-11675 (2015-07-07)
During the anaerobic digestion of dewatered sludge, polyacrylamide (PAM), a chemical conditioner, can usually be consumed as a carbon and nitrogen source along with other organic matter (e.g., proteins and carbohydrates in the sludge). However, a significant accumulation of acrylamide
Articles
Highlighting existing and novel fabrication methods for both, solid and hydrogel-based scaffold for tissue engineering applications.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service