687529
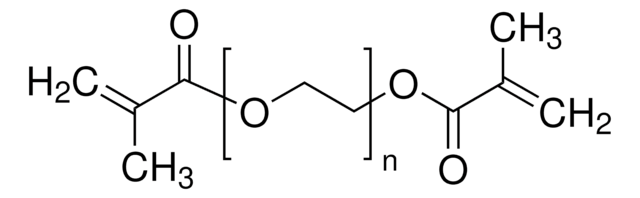
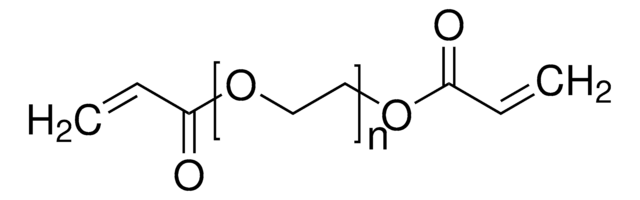
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate
average MN 2,000, cross-linking reagent polymerization reactions, methacrylate, ~1000 ppm MeHQ as stabilizer
Synonym(s):
Polyethylene glycol, PEG dimethacrylate
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate, average Mn 2000, contains ~1000 ppm MeHQ as stabilizer
form
powder
Quality Level
mol wt
average Mn 2000
contains
~1000 ppm MeHQ as stabilizer
reaction suitability
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
bp
>200 °C/2 mmHg (lit.)
transition temp
Tm 49-55 °C
Mw/Mn
<1.2
Ω-end
methacrylate
α-end
methacrylate
polymer architecture
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
OCCO.CC(=C)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H14O4/c1-7(2)9(11)13-5-6-14-10(12)8(3)4/h1,3,5-6H2,2,4H3
InChI key
STVZJERGLQHEKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Highlighting new synthetic modifications of PEG to improve the mechanical properties and degradation of resulting hydrogels in tissue engineering applications.
In this article, we will discuss the benefits and limitations of several 2D and 3D scaffold patterning techniques that can be applied in the presence of cells. Although these methods will be discussed in the context of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-based hydrogels, they can technically be applied to any optically transparent, photoactive substrate.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service