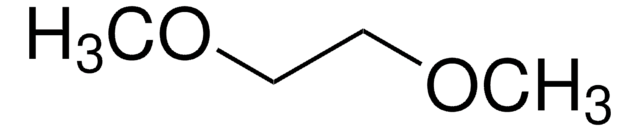
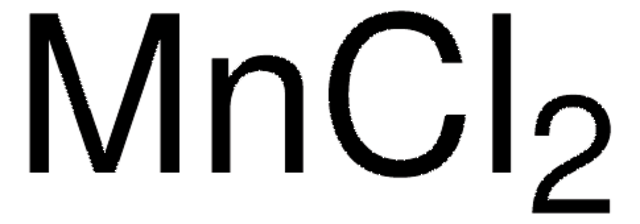450936
Iron(II) chloride
AnhydroBeads™, −10 mesh, 99.99% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Ferrous chloride, Iron dichloride
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
FeCl2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
126.75
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352302
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
product line
AnhydroBeads™
Quality Level
Assay
99.99% trace metals basis
impurities
≤150.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
particle size
−10 mesh
mp
677 °C (lit.)
density
3.16 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
application(s)
battery manufacturing
SMILES string
Cl[Fe]Cl
InChI
1S/2ClH.Fe/h2*1H;/q;;+2/p-2
InChI key
NMCUIPGRVMDVDB-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. It has significant applications in solar cells, fuel cell catalysts, and semiconductors due to its unique properties. Additionally, it can also act as a reducing agent in redox reactions, which are crucial in many electrochemical processes.
Application
Iron(II) chloride can be used as:
- A doping agent in the fabrication of mixed organic-inorganic perovskite for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells. The incorporation of iron(II) chloride improve the overall efficiency of the solar cell.
- A precursor for synthesizing various iron(II) coordination complexes. These complexes are significant due to their unique optical and electronic properties, which are essential for various applications, including solar energy conversion and catalysis.
- As a precursor in the synthesis of iron-nitrogen-carbon (Fe–N–C) catalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells.
Legal Information
AnhydroBeads is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
accessory
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
8B - Non-combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
does not flash
Flash Point(C)
does not flash
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Inorganic Chemistry, 37, 612-612 (1998)
Chong Qin et al.
Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 51(28), 6971-6975 (2012-06-13)
Ironing it out: an efficient and convenient nitrogenation strategy involving C-C bond cleavage for the straightforward synthesis of versatile arylamines is presented. Various alkyl azides and alkylarenes, including the common industrial by-product cumene, react using this protocol. Moreover, this method
Qand Agha Nazari et al.
Journal of pharmacological sciences, 120(2), 105-111 (2012-09-29)
Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) is widely used as a potent vasodilator and a nitric oxide (NO) donor, whereas the cytotoxicity of SNP has been well documented. SNP releases several potentially toxic products such as cyanide anion, NO, and iron. We investigated
Qinqin Xia et al.
The Journal of organic chemistry, 77(20), 9366-9373 (2012-10-03)
Iron-catalyzed direct C-N bond formation between azoles and amides is described. The oxidative coupling reactions of sp(3) C-H bonds adjacent to a nitrogen atom in amides and sulfonamides with the N-H bond in azoles proceeded smoothly in the presence of
Jiangfei Meng et al.
Journal of food science, 77(1), C8-14 (2011-12-21)
Wines made from 3 spine grape (Vitis davidii Foex) genotypes-Junzi 1# (JZ 1#), Junzi 2# (JZ 2#), and Liantang (LT)-and Cherokee rose (Rosa laevigata Michx., CR) were evaluated for their phenolics composition and antioxidant activities by several assays, including 2,2'-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service