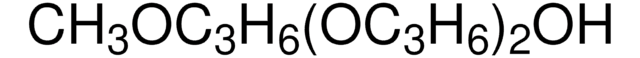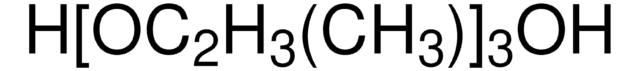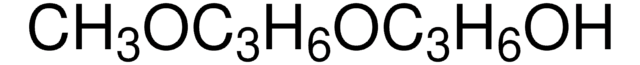302864
Tri(propylene glycol) methyl ether, mixture of isomers
96%
Synonym(s):
O-Methyltripropylene glycol, [2-(2-Methoxymethylethoxy)methylethoxy]propanol, methylpropylene triglycol
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
CH3(OC3H6)3OH
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
206.28
EC Number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
96%
form
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.43 (lit.)
bp
100 °C/2 mmHg (lit.)
density
0.968 g/mL at 25 °C
InChI
1S/C10H22O4/c1-8(5-11)14-10(3)7-13-9(2)6-12-4/h8-11H,5-7H2,1-4H3
InChI key
GVZNXUAPPLHUOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Tri(propylene glycol) methyl ether is a promising oxygenating agent for diesel fuels. Bubble coalescence and post-rupture oscillation in tri(propylene glycol) methyl ether solutions using high-speed cinematography was studied.
Application
- Composition-explicit distillation curves of diesel fuel with glycol ether and glycol ester oxygenates: fuel analysis metrology to enable decreased particulate emissions.: This study by Smith, Ott, and Bruno explores the application of glycol ethers, including tri(propylene glycol) methyl ether, in diesel fuels. The research demonstrates how these oxygenates can decrease particulate emissions, providing a valuable insight into the environmental benefits and performance improvements of glycol ethers in fuel formulations (Smith et al., 2008).
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
113 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
G Bournival et al.
Journal of colloid and interface science, 414, 50-58 (2013-11-16)
Most processes involving bubbling in a liquid require small bubbles to maximise mass/energy transfer. A common method to prevent bubbles from coalescing is by the addition of surfactants. In order to get an insight into the coalescence process, capillary bubbles
Beverly L Smith et al.
Environmental science & technology, 42(20), 7682-7689 (2008-11-06)
We recently introduced several important improvements in the measurement of distillation curves of complex fluids. The modifications to the classical measurement provide for (1) a composition-explicit data channel for each distillate fraction (for both qualitative and quantitative analysis), (2) temperature
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service