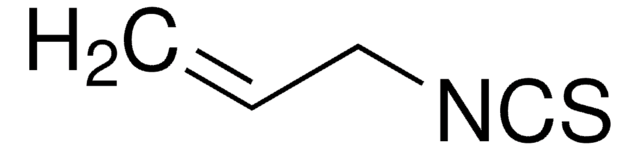
171573
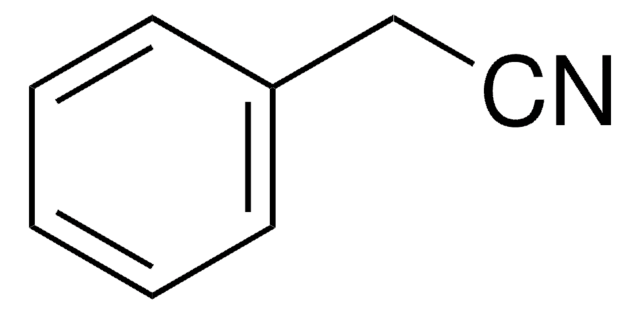
3-Phenylpropionitrile
99%
Synonym(s):
Hydrocinnamonitrile
About This Item
Recommended Products
Assay
99%
form
liquid
refractive index
n20/D 1.521 (lit.)
bp
113 °C/9 mmHg (lit.)
mp
−2-−1 °C (lit.)
density
1.001 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
functional group
nitrile
phenyl
SMILES string
N#CCCc1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C9H9N/c10-8-4-7-9-5-2-1-3-6-9/h1-3,5-6H,4,7H2
InChI key
ACRWYXSKEHUQDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
230.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
110 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service