All Photos(2)
About This Item
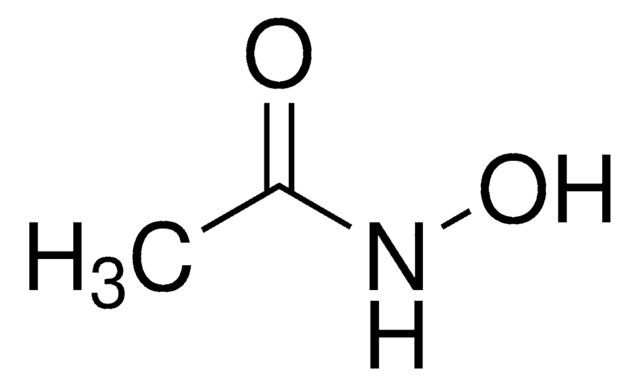
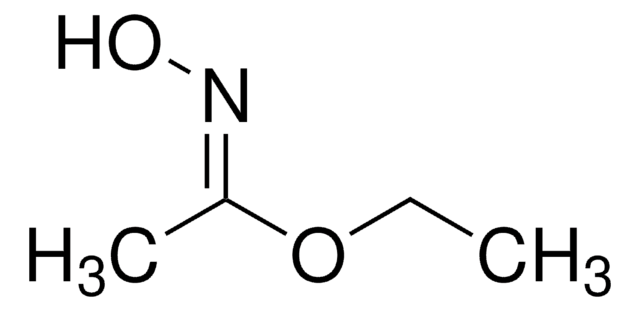
Linear Formula:
CH3CONHOH
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
75.07
Beilstein:
1739019
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
mp
88-90 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC(NO)=O
InChI
1S/C2H5NO2/c1-2(4)3-5/h5H,1H3,(H,3,4)
InChI key
RRUDCFGSUDOHDG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... CA2(760) , MMP3(4314)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Acetohydroxamic acid is a potent inhibitor of bacterial urease activity and reduces urinary ammonia levels. 2-Acetohydroxamic acid loaded floating microspheres forms an efficient drug delivery system for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori.
Application
Acetohydroxamic acid was used:
- to study the mechanism of complexation of iron (III) with acetohydroxamic acid
- to study the inhibitory mechanism of lansoprazole and omeprazole on Helicobacter pyloni
- in urease inhibition studies
- for in situ generation of nitrosocarbonylmethane as a Diels-Alder dienophile
Used in urease inhibition studies and for in situ generation of nitrosocarbonylmethane as a Diels-Alder dienophile.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Repr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
K Nagata et al.
Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 37(4), 769-774 (1993-04-01)
The gastric proton pump inhibitor lansoprazole, its active analog AG-2000, and omeprazole dose dependently inhibited urease activity extracted with distilled water from Helicobacter pylori cells; the 50% inhibitory concentrations were between 3.6 and 9.5 microM, which were more potent than
Zbl. Bakt., 275, 63-63 (1991)
D P Griffith et al.
The Journal of urology, 140(2), 318-324 (1988-08-01)
Acetohydroxamic acid is known to inhibit bacterial urease activity, thus, reducing urinary ammonia levels. A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of acetohydroxamic acid was conducted at 12 Veterans Administration spinal cord injury units. A total of 210 male spinal cord injury
Journal of the Chemical Society. Perkin Transactions 1, 1001-1001 (1991)
Mechanism of iron (III) complex formation. Activation volumes for the complexation of the iron (III) ion with thiocyanate ion and acetohydroxamic acid.
Funahashi S, et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 22(14), 2070-2073 (1983)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service