All Photos(1)
About This Item
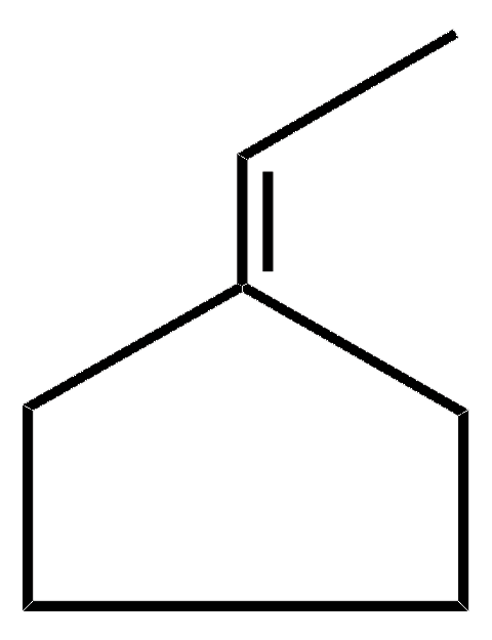
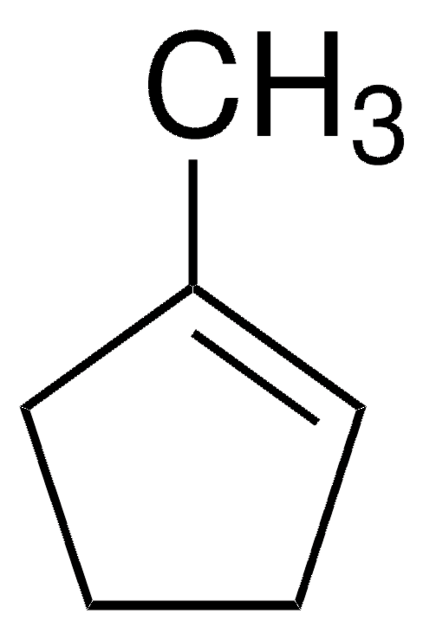
Linear Formula:
C6H10(=CHCH3)
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
110.20
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99%
refractive index
n20/D 1.462 (lit.)
bp
136 °C (lit.)
density
0.822 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
C\C=C1\CCCCC1
InChI
1S/C8H14/c1-2-8-6-4-3-5-7-8/h2H,3-7H2,1H3
InChI key
BPBOWYWUOUJKLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Ethylidenecyclohexane is oxidized by purified ethylbenzene dehydrogenase.
Application
Ethylidenecyclohexane has been used as a substrate in the Lewis-acid catalyzed reactions of azodicarboxylates with different alkenes.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Liq. 3
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
75.2 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
24 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
H A Johnson et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 183(15), 4536-4542 (2001-07-10)
The first step in anaerobic ethylbenzene mineralization in denitrifying Azoarcus sp. strain EB1 is the oxidation of ethylbenzene to (S)-(-)-1-phenylethanol. Ethylbenzene dehydrogenase, which catalyzes this reaction, is a unique enzyme in that it mediates the stereoselective hydroxylation of an aromatic
Pompiliu S Aburel et al.
Organic & biomolecular chemistry, 3(12), 2344-2349 (2005-07-13)
Lewis acids such as Cu(OTf)(2), Zn(OTf)(2), Yb(OTf)(3) and Nd(OTf)(3) catalyze the aza-ene reaction of alkenes with azodicarboxylates, giving the allylic amination adducts. The use of bis(2,2,2-trichloroethyl)azodicarboxylate as the amination reagent and Cu(OTf)(2) and Yb(OTf)(3) as the catalysts gave the aza-ene
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service

![TRICYCLO[3.3.2.0(2,8)]DECA-3,6,9-TRIENE AldrichCPR](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/514/889/34159289-e30a-4073-a31a-08ee96a8d1c3/640/34159289-e30a-4073-a31a-08ee96a8d1c3.png)