Enzymes for Alternative Energy Research
We are committed to help unlock the today’s challenge of releasing the energy of glucose that nature has cleverly locked into lignocellulosic biomass. To the untrained eye, starch and cellulose structures appear almost identical. Yet the barriers between cellulosic biomass hydrolysis and ethanol production have proven to be orders of magnitude more challenging than with starch-like biomass.
Although many of the biochemical aspects of these challenges are well understood, they remain an enigma of nature. The two main, and closely related hinderences to the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic polymers are; How do we physically dismantle biomass on a molecular level to yield cellulosic polymers available to hydrolysis by cellulase and other glycolytic enzymes? How do we penetrate the barrier posed by the closely integrated network of liginins surrounding cellulose microfibrils?

Cellulases and Related Enzymatic Activities
Cellulase
EC# 3.2.1.4
Synonyms: 1,4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase
Cellulase catalyzes the endohydrolysis of 1,4-β-D-glucosidic linkages in cellulose, lichenin and cereal β-D-glucans
Many commercial cellulase preparations contain various classes of cellulases and related activities.
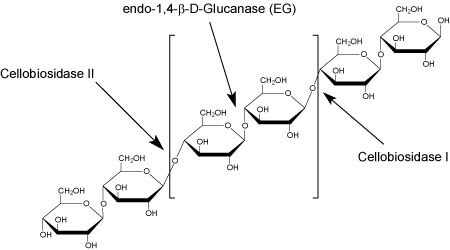
Cellulase Activities
- The endo-1,4-β-D-glucanases (EGs) cleave cellulose in it's internal non-terminal regions, yielding oligosaccharides
- The two forms of cellobiohydrolases (CBH) are considered exo-1,4-β-D-glucanases, releasing cellobiose disaccharides from the cellulose chain reducing end (CBHI), and non-reducing end (CBHII)
- β-Glucosidase is an exo-hydrolase that yields glucose monosaccharides from soluble oligosaccharaides such as cellobiose
- Other activities that can be found in cellulase preparations include xylanase, hemicellulase, and laminarinase
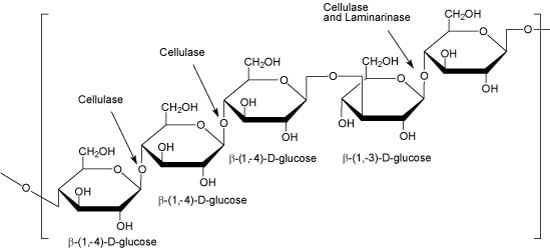
Cerial β-Glucan, Polymer of β-(1,4) glycopyranosyl units occring as predomiantly cellotriose and cellotetraose separated by single β-(1,3)-Dglycopyranosyl units. Cross-linking can occur within the consecutive cellotriose regions.
from Aspergillus sp.
Product Number C2605 (Carezyme® 1000 L)
from Aspergillus niger
Product Number C1184 (powder, min. 0.3 un/mg)
from Trichoderma reesei
Product Number C8546 (powder, min. 1.0 un/mg)
Product Number C2730 (Celluclast® 1.5 L)
from Trichoderma viride
Product Number C0615 (Yakult Onozuka RS)
Product Number C1794 (cell culture tested, powder, min. 3.0-10 un/mg)
Cellobiohydrolase I
from Hypocrea jecorina
Product Number E6412 (recombinant expressed in corn)
Driselase
from Basidiomycetes sp.
Product Number D9515 (Crude powder containing laminarinase, xylanase and cellulase)
Endoglucanase
from Acidothermus cellulolyticus
Product Number E2164 (recombinant, expressed in corn)
Laminarinase
EC# 3.2.1.6
Synonyms: endo-1,3(4)-β-glucanase
Laminarinase catalyzes the endohydrolysis of 1,3- or 1,4-linkages in β-D-glucans when the glucose residue whose reducing group is involved in the linkage to be hydrolysed is itself substituted at C-3
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?