P4406
Papain Agarose from papaya latex
lyophilized powder, 90-150 units/mL packed gel
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
papaya (latex)
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
90-150 units/mL packed gel
mol wt
21 kDa
extent of labeling
3,000-5,000 units per g agarose (at pH7.0 at 30 °C.)
matrix
beaded agarose
storage temp.
−20°C
Application
Papain is used in dissecting solutions. It is used to produce Fab fragments of antibodies. It is used for cell dissociation since it has been shown to be more effective and less damaging with certain tissues. Papain has been used to isolate morphologically intact cortical neurons from postnatal rats. Limited papain digestion is used for structural studies of enzymes and other proteins. In addition, papain is used in red cell serology to modify the red cell surface to enhance or destroy the reactivity of many red cell antigens. Papain is useful for platelet serology studies. Papain has also been used in the enzymatic synthesis of amino acids, peptides, and other molecules. Product P4406 is agarose-linked papain and is provided as a lyophilized powder stabilized with lactose. Product P4406 has been used to digest purified anti-JMJD6 hamster monoclonal antibody into Fab fragments.
Used to produce Fab fragments of antibodies. Also used for cell dissociation since it has been shown to be more effective and less damaging with certain tissues.
Biochem/physiol Actions
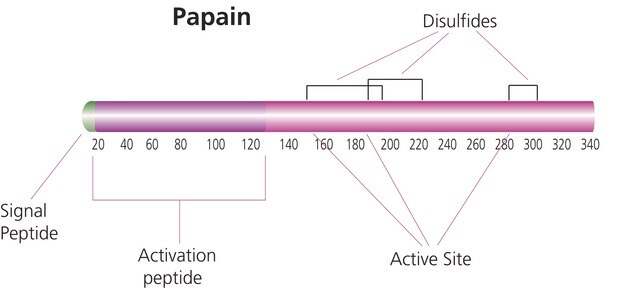
Papain papaya latex has antifungal activity against C. albicans. It is a cysteine protease that cleaves peptide bonds of basic amino acids, leucine, or glycine.
. The pH optimum is 6.0-7.0
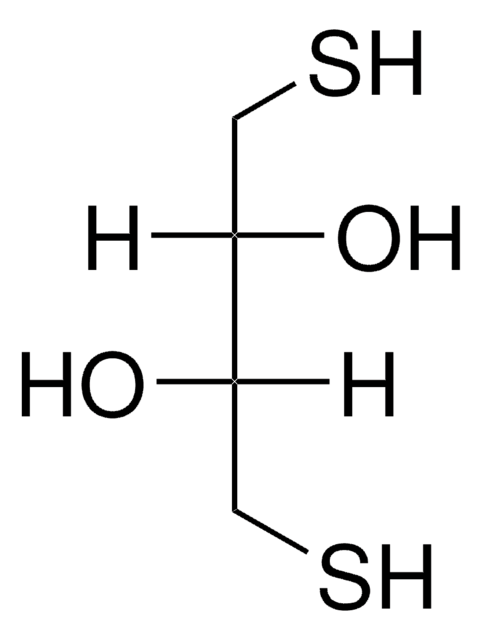
. Papain hydrolyzes esters and amides. Papain consists of a single polypeptide chain with three disulfide bridges and a sulfhydryl group necessary for activity of the enzyme.
. The pH optimum is 6.0-7.0
. Papain hydrolyzes esters and amides. Papain consists of a single polypeptide chain with three disulfide bridges and a sulfhydryl group necessary for activity of the enzyme.
A cysteine protease that cleaves peptide bonds of basic amino acids, leucine or glycine. pH optimum 6.0-7.0
Also hydrolyzes esters and amides.
Also hydrolyzes esters and amides.
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of BAEE per min at pH 6.2 at 25°C, unless otherwise indicated below.
Physical form
Lyophilized powder, stabilized with lactose
inhibitor
Product No.
Description
Pricing
substrate
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Xia Hong et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(33), 14568-14572 (2010-08-04)
JMJD6 is a Jumonji C domain-containing hydroxylase. JMJD6 binds alpha-ketoglutarate and iron and has been characterized as either a histone arginine demethylase or U2AF65 lysyl hydroxylase. Here, we describe the structures of JMJD6 with and without alpha-ketoglutarate, which revealed a
Y. Ozari et al.
Journal of the Chemical Society. Chemical Communications, 295-295 (1974)
Articles
Papain is a cysteine protease of the peptidase C1 family. Papain consists of a single polypeptide chain with three disulfide bridges and a sulfhydryl group necessary for activity of the enzyme.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service