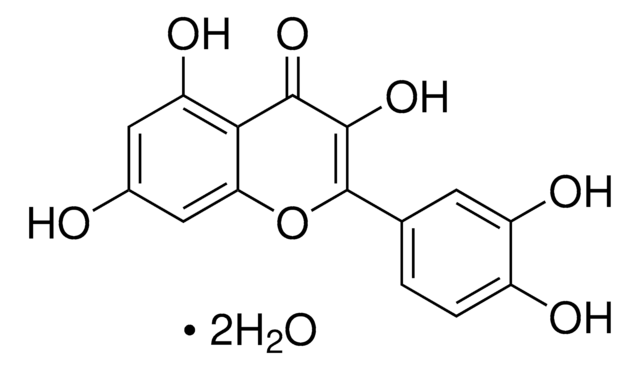
K0133
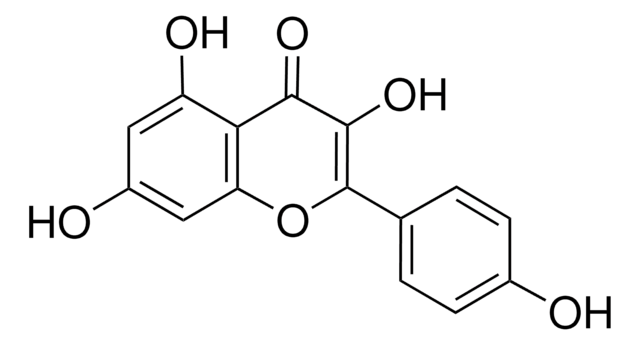
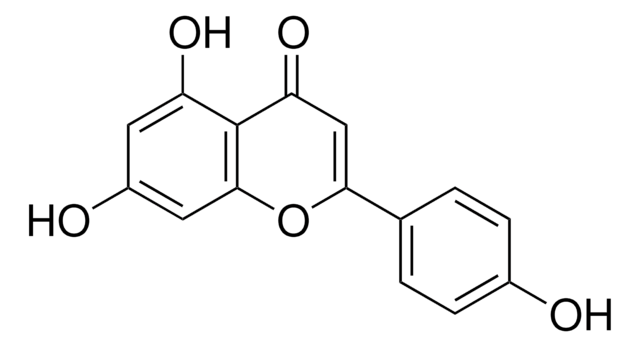
Kaempferol
≥90% (HPLC), powder
Synonym(s):
3,4′,5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone, 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, Robigenin
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic
Assay
≥90% (HPLC)
form
powder
storage condition
protect from light
color
yellow
mp
277 °C
solubility
ethanol: 20 mg/mL
DMSO: 50 mg/mL
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
Oc1ccc(cc1)C2=C(O)C(=O)c3c(O)cc(O)cc3O2
InChI
1S/C15H10O6/c16-8-3-1-7(2-4-8)15-14(20)13(19)12-10(18)5-9(17)6-11(12)21-15/h1-6,16-18,20H
InChI key
IYRMWMYZSQPJKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... CDC2(983) , CDK5(1020) , CDK6(1021) , CYP1A2(1544) , CYP2C9(1559) , GSK3A(2931)
mouse ... Hexa(15211)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- to check its potential effect as an antioxidant and neuroprotective agent against rotenone-induced Parkinson′s disease (PD) model in SH-S5Y5 cells
- to test its anti-inflammatory effect on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory injury in human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs)
- to study its apoptosis sensitizing effect on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells by inhibiting nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Packaging
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
Antioxidants protect biological systems from oxidative damage produced by oxygen-containing free radicals and from redoxactive transition metal ions such as iron, copper, and cadmium.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service